The Internet is a rather subversive and aggressive ideology and system. Since its birth, it has struck multiple industries across borders and achieved great success in just over a decade. To sum up, the core idea of ​​the Internet is economies of scale, to form economic effects on scale, that is, in the initial stage, large-scale capital investment is made, products that meet basic needs are provided, and customers are developed on a large scale in order to achieve economies of scale. After reaching a certain scale, it began to diversify and batch replicate this scale economy to form a diversified scale development. Because the cost of storage and marketing for each new product added to the Internet can approach zero, the nature of the Internet determines that it is naturally aggressive and subversive for various industries.
After the Internet gradually developed into the field of industrial control systems, marketing concepts and systems such as the Industrial Internet, Industry 4.0, and the Industrial Internet of Things were born. These concepts are on the ups and downs, and the city is full of ups and downs for a while. After the hustle and bustle, it may be quiet, but the *** from the Internet is unstoppable.
The general trend of the world is vast, and those who follow it will prosper, and those who oppose it will perish. As practitioners of industrial control systems, we should put aside the fog of marketing concepts and pursue the technological changes of industrial control systems under the Internet concept. In this era of change, the realization of the concepts and technologies advocated by Industry 4.0, Smart Factory, Industrial Internet, etc. will have to be reconfigured in a short time. Therefore, the core equipment PLC of the industrial control system needs to be reconfigured flexibly. How to flexibly configure PLC has become the backing support for the industrial Internet to truly realize industrial interconnection. Therefore, from this perspective, this article describes the core technology behind the Industrial Internet in the age of the Industrial Internet.

Programmable logic controllers, called Programmable Logic Controllers in English, and PLCs for short (hereafter referred to as PLCs in this article) are small industrial computers with modular components designed to automate customized control processes. The control process I understand is the process of controlling physical equipment through programs, and this program is implemented in the form of logical expression (ladder diagram or other PLC programming languages). In the PLC, the real physical device is logically represented by a symbol or character string, so the written program is a process of programming and combining these logics and sequential control. This control process is programmable and customizable. So it is called a programmable logic controller (PLC).
PLC has been developing and has not yet given a final definition to it. The International Electrotechnical Institute (IEC) issued the first, second and third drafts of the PLC standard in November 1982, January 1985 and February 1987. In the third draft, the PLC is defined as follows: Programmable logic controller (PLC) is a digital operation electronic system designed for application in an industrial environment. It uses a programmable memory to store instructions for operations such as logic operations, sequence control, timing, counting, and arithmetic operations, and control various types of machinery through digital and analog input and output. Or the production process. The programmable logic controller (PLC) and its related peripheral equipment should be designed according to the principle of being easy to form a whole with the industrial control system and easy to expand its functions.
In the field of industrial control systems, the physical machines and production lines in the industrial production environment are usually controlled by hardware PLCs. This is also considered the current optimal solution and has driven the process of industrial automation for many years. To better understand the purpose of PLC, let us look at a brief history of PLC.
Industrial automation started before PLC. In the early to mid-twentieth century, industrial automation was usually implemented using complex electromechanical relay circuits. An electromechanical relay is an electronic control device, which has a control system (also called an input loop) and a controlled system (also called an output loop). When the input (such as voltage, current, temperature, etc.) reaches a specified value, it will be controlled The output circuit of the electrical appliance is turned on or off. However, there are many problems with the number of relays, wires, and space required to manufacture simple automation through the relay structure. The realization of a simple factory control process requires thousands of relays! If there is something in the logic circuit that needs to be changed, it is even more catastrophic.
In 1968, the first programmable logic controller (PLC) came out, replacing the industrial automation control realized by the complex relay circuit in industrial production. The first to put forward a clear idea was General Motors. In 1968 they wanted a device that could replace the relay control. The following year, American Digital Equipment Corporation developed the first programmable controller PDP-14 for General Motors, and the trial was successful. This was the world's first PLC. By the late 1970s, PLC began to enter a stage of rapid development, with a rapid increase in operating speed and substantial progress in miniaturization. It began to be widely used in Western countries in the early 1980s and grew rapidly. That period can be described as the golden age of PLC. Later, mainframes and ultra-small computers were developed. In the 21st century, the scale of PLC continues to expand, the number of I/O points increases, multiple CPUs work in parallel, large-capacity storage, high-speed scanning, etc. Modularization and standardization have become the mainstream, the cost has been greatly reduced, and the application has become more extensive.
The PLC design allows control engineers and technicians who are familiar with relay logic and control schematics to easily program. One of the initial implementations is ladder logic, which is designed to simulate control circuit schematics. The ladder diagram looks like a control circuit, in which electricity from left to right energizes the relay coil by closing the contacts. As shown in Figure 1 below:
Figure 1-Ladder diagram logic example
The ladder diagram in the above figure looks like a simple control circuit schematic diagram. The left side shows the input sources such as switches, buttons, and sensors, and the right side shows the output sources. Through such intuitive interface programming such as ladder logic to realize complex automation process, it is more convenient and efficient than using the previous relay, and the learning cost of transition to PLC is also reduced to a minimum. PLC is the product of the combination of microcomputer technology and traditional relay contact control technology. It overcomes the shortcomings of complicated wiring of mechanical contacts in the relay contact control system, low reliability, high power consumption, and poor versatility and flexibility. Make full use of the advantages of microprocessors, and take care of the skills and habits of on-site electrical operation and maintenance personnel, especially PLC programming, which does not require special computer programming language knowledge, but uses a set of relay ladder diagrams as the basis. The simple instruction form makes the user programming vivid, intuitive, convenient and easy to learn; debugging and error checking are also very convenient. After purchasing the required PLC, the user only needs to do a small amount of wiring and simple user programming according to the instructions of the manual, and then the PLC can be applied to production practice flexibly and conveniently.
For programming based on such ladder logic, it is only necessary to control the programming ladder logic according to the production process of the on-site factory environment, so as to realize the programmability of the control process. Although this programmable logic controller (PLC) is programmable, there are still some differences from today's hyped software definition, mainly because the programmable logic controller (PLC) has certain restrictions on its programmability. That is, each programmable logic controller (PLC) needs to be programmed by a specific programming software after the program is implemented, and then the final control process program is uploaded through communication with the programmable logic controller (PLC). Programmable logic controller (PLC) is between traditional hardware equipment and software definition, and realizes the programmability of the data plane, but the control plane is not separated to realize unified centralized control.
PLC was developed to cope with the complicated machine control of electromechanical relays. The goal is to develop a more flexible control system, reduce machine downtime, and use this new device to perform logic functions. From the PLC development to the present, the original design and development goals have indeed been achieved. PLCs have been silently dedicated to the field of industrial automation for decades. Even in applications that are critical to safety, they have achieved the reliability of controlling machines. As a result, almost all modern industrial automation controllers are realized by PLC. In an industrial environment, PLC is almost omnipotent.
Second, the development trend of industrial control systemsThe first industrial revolution occurred in the 18th to 19th centuries, and improved the production process by creating new manufacturing processes to promote social progress. At that time, the manufacturing industry mainly relied on the production of goods by hand. The first industrial revolution, which was born in the United Kingdom, changed this situation and enabled the machine manufacturing industry to make better use of water and steam power to promote productivity. And these improved innovative ideas and systems naturally played a big role in the second and third industrial revolutions. The ongoing industrial revolution is the fourth industrial revolution, also known as Industry 4.0 (proposed in Germany) or Industrial Internet (proposed in the United States). The basic concept of Industry 4.0 is the same as other industrial revolutions: by improving business processes and manufacturing processes, reducing production time, reducing production material costs, reducing the number of defective products, and making industrial manufacturing easier by creating machines that can replace human work. .
Industry 4.0 or Industrial Internet is the term for the ongoing industrial revolution. It originally referred to the digitization of manufacturing, but in fact it also refers to the digitization of other industries such as medical, logistics, oil and gas. It also refers to the concepts we often hear about smart factories, smart cities or smart devices. Industry 4.0 is about the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), Cyber-Physical System (CPS), Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT). Among them, the change is first initiated in the field of information technology, cloud computing, machine learning and big data, etc. IT technology guides modern information companies to adopt new business models, improve their own business processes and operational efficiency, and enhance their core competitiveness. The development of these new IT technologies has solved a common demand of Internet companies and traditional companies, that is, to solve the challenges of continuous scale expansion and rapid business changes, while also effectively controlling costs. Among traditional companies, other types of companies are willing to take risks by deploying new technologies at an early stage, while industrial companies may be more cautious. Due to the particularity of the industrial environment, it is still unknown whether this demand of industrial enterprises can learn from the success of Internet enterprises. In order to overcome this threshold, the industry needs innovation. Therefore, the rise of concepts and systems like Industry 4.0 is aimed at conducting a lot of research, testing, and implementing these technological changes to guide industrial enterprises.
Regarding the latest progress in practice, we will explain it by analyzing the traditional automated pyramid model. The traditional automation pyramid (Figure 2) represents a typical model in the field of industrial control systems today. All physical devices from sensors to actuators are at the field level, and the data and actions used to control these field-level physical devices are at the second level. The second level uses physical hardware such as PLC to control the field-level physical hardware. The third level is a data acquisition and monitoring level, allowing users to monitor and control their industrial control process through the SCADA system. SCADA is the abbreviation of Data Acquisition and Monitoring Control System. A typical SCADA architecture includes the first three levels of the traditional automation pyramid. MES and ERP systems are based on SCADA architecture. MES stands for Manufacturing Execution System, which refers to a system that monitors manufacturing data in real time. The MES system can track the cargo situation of the entire production process. The enterprise resource planning (ERP) system provides the highest level of the automation pyramid. The ERP system manages real-time monitoring of core business processes, such as production or product planning, material management and financial conditions.
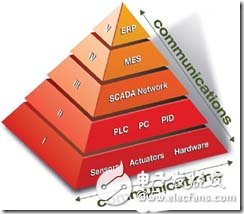
Figure 2-Traditional Automation Pyramid
After the arrival of Industry 4.0 and cyber-physical systems, the traditional industrial control system architecture based on the pyramid model is undergoing changes. First, the top-level ERP and MES gradually realize interconnection and integration, realizing the upper-level linkage of production data, and finally using the advantages of cloud computing, big data and even artificial intelligence data storage and computing to deeply mine and process production data. And finally output optimized production data to improve production efficiency. The equipment and systems in the lower production execution layer are also in the stage of intelligence and reconstruction, such as the terminal of the final production data and the changes that occur, including the running shoes that people wear, the smart production line in the smart factory, and these from sensors to actuators. All of the physical devices have been developing in the direction of digitization and intelligence and have achieved results. Therefore, it can be found that in the age of Industrial Internet or Industry 40, the ultimate system transformation of industrial control system is to transform the traditional pyramid model from both ends. To be precise, the Industrial Internet focuses on the technological change of the upper-level production data, that is, the integration of industrial control systems and cloud computing, big data, artificial intelligence, etc., and advocates uploading industrial control system data to the industrial cloud, and use the cloud to perform Data mining and analysis to optimize the production process. Therefore, in the implementation of the current industrial Internet architecture, the implementation of the system architecture is either the industrial Internet platform directly collects the production data on the PLC with the PLC equipment, or the industrial Internet platform collects the data in the real-time database of the industrial control system, or the development A data acquisition gateway is created. After all data is collected through the data acquisition gateway, the gateway uploads the data to the industrial Internet platform. So the Industrial Internet is essentially a collection of industrial control system data on a cloud computing platform. Industry 4.0 focuses on realizing the digitization and intelligence of all physical devices at the bottom from sensors to actuators, and realizing that these terminal devices directly upload the data. The uploaded platform may be MES, and the historical database may also be an industrial Internet platform. For most companies, the first step for Industry 4.0 is to vertically integrate and digitize all relevant subsystems of the production system through the MES system to achieve real-time factory operation transparency. At the same time, horizontal integration also includes the connection of functional areas. Here, MES functions as the core element of the information carousel, collecting, analyzing, and processing big data, as well as supporting data exchange with other systems.
Before the birth of automated control, the production of systems and machines had to rely on manual operations. The advantage of automation is that the links that require repeated operations are realized by automatic control, which frees people's hands and realizes many advantages-from shortening the time to market to reducing the failure of products, the advantages of automatic control can be well demonstrated. . Nevertheless, with the continuous growth of market demand, people still dislike the existing automation control that cannot meet the demand for production efficiency, and the essence is the same. People need more flexibility to ensure rapid product production and marketing. Flexibility is now the key and focus of industrial automation. These flexibility are manifested in: more and more factory data should be reusable, logic codes should be easy to move and reusable, systems should be modular and extensible, and production companies should choose them according to their own needs. The preferred supplier instead of the current binding sales and so on.
These realizations of Industrial Internet and Industry 4.0 support the flexibility and scalability requirements of future industrial control systems. The Industrial Internet enables large-scale and centralized storage of our production data, realizing big data that was impossible before, and using the unprecedented computing power of the cloud computing platform to analyze these big data, mining and optimizing production efficiency. Industry 4.0 has made field devices, machines and factories "smarter", so we can talk about smart devices, smart machines, and smart factories. However, we will find that neither Industrial Internet nor Industry 4.0 has made any further technological changes to the "brain" PLC of industrial control systems. This phenomenon of heavy weight at both ends and light weight in the middle is like a toll station on a highway. The widening of the highway is far from being able to achieve greater vehicle throughput. The toll stations standing on the highway are the bottleneck points on this road. . Therefore, it is now necessary to set up more toll windows, implement electronic toll collection and other measures for toll stations to adapt to the rapid and rapid growth of traffic flow. The same applies to the field of industrial control systems. The core PLC equipment of control cannot be flexibly expanded. Undoubtedly, this limitation will greatly weaken the flexibility and scalability of industrial control systems.
Therefore, the current industry's exploration of technical systems for Industrial Internet, Industry 4.0, etc., will focus on PLC.
Specifically, there are two main schemes for realizing PLC flexibility and scalability:
1. Realize PLC virtualization. Using PLC virtualization is a virtual PLC (vPLC) to replace traditional hardware PLC;
2. PLC hardware reconstruction, to realize the next generation of new and intelligent PLC equipment, replacing the traditional hardware PLC.
These two technologies are the current technical hotspots and research directions for the transformation of industry to the Internet. At least from the perspective of theoretical realization, the realization of PLC virtualization will protect the existing interests of most existing manufacturers and their users to the greatest extent, and Based on the successful cases of the information system, everyone is full of confidence in its realization. In addition, PLC hardware reconstruction, mainly based on the software definition idea, separates the logic operation plane and the logic control plane of the PLC hardware. The PLC hardware will realize the general logic operation, and the logic control and logic of the control plane will be unified by the controller. management.
3. Virtualization and software definition of PLCVirtualization and cloud computing have achieved great success in the ICT field, and their degree of innovation has even subverted the entire old ICT architecture system, turning it all over from the inside out. The effect is also quite significant. At least the operating cost of the current ICT environment has been significantly reduced using virtualization and cloud computing technology. As for how much to reduce and to what extent, I believe this is a number that is difficult to adjust. But at least companies that use virtualization and cloud computing have already enjoyed the benefits they bring, and the current virtualization and cloud computing technologies have become the most advanced solutions in the office and corporate world. But it is not easy to deploy these technologies and solutions in industrial applications, because in an industrial environment, the requirements are usually very high, and system failures and real-time performance are critical to industrial production and applications. The Industrial Internet and Industry 4.0 were originally to solve the transformation and technical realization of advanced IT innovation technologies such as virtualization and cloud computing to be applied to the industrial field and to improve industrial production efficiency. In the practice of Industrial Internet and Industry 4.0, are the technologies of Industrial Internet and Industry 4.0 currently so developed and reliable that they can be used in industrial control environments that need to meet higher requirements such as stability and real-time computing? , This is questionable. However, judging from some publicly published cases and statistical data, manufacturers have begun to benefit from Industrial Internet and Industry 4.0 technologies. These benefits are mainly the use of Industrial Internet or Industry 4.0 technologies. They can use real-time production data to help more Effectively plan the production process to improve production efficiency and reduce operating costs. The success of these cases has encouraged people to actively invest in research and development of the next technological solution and improve the current technology implementation while being encouraged. At present, industrial control equipment manufacturers such as Siemens and virtualized cloud computing vendors engaged in the IT field are all focusing on trying to virtualize the control plane, using software instead of physical hardware to reduce operating costs, and have a more flexible control environment. PLC virtualization or software-defined PLC, in other words, using virtual PLC (vPLC) or software-defined PLC is their next research and realization goal. At least from the current technology realization and research direction and IT's successful experience, the general trend is like this.
The technical idea of ​​PLC virtualization or software-defined PLC is to decouple traditional dedicated hardware functions. Because in the age of Industrial Internet or Industry 4.0, data integration of machines with higher-level applications in the factory floor is mainly done using traditional protocols, which lack support for the flexible integration of new devices. There is always a contradiction between the two. How to resolve this contradiction? Only an intermediate layer can be introduced between the two, and the control logic and the machine can be separated by virtualized PLC controller or software-defined PLC, and more flexible reconfiguration can be obtained.
PLC virtualization or software-defined PLC allows users to replace or add components without affecting other parts of the system, enabling easy scalability and system modularity. PLC virtualization or software-defined PLC is designed as an open platform that allows users to choose preferred components and solutions, which means users can flexibly choose different suppliers (no supplier lock-in). In the Industry 3.0 system, it is not so easy or impossible to use components from multiple vendors in the same architecture. There is usually no hardware dependency in PLC virtualization or software-defined PLC, so it is easy to migrate and reuse software. PLC virtualization or software-defined PLC uses virtualization or software-defined technology, using more software instead of hardware, because the amount of hardware required is less, so it reduces the cost and reduces the space occupied. The goal is to provide off-the-shelf and available for sale COTS (COTS = commercial off-the-shelf) software/hardware products to achieve flexible selection and scalability of the overall solution. Virtualization technology and software-defined architecture is a software-centric model, which has advantages in system centralized management, network processing, and security. Remote monitoring reduces operating costs, and maintenance engineers or operators do not always need to check the status of the machine on site. Centralized management simplifies remote monitoring because you only need to access a software platform to manage your assets. Through cloud computing and the use of smart sensors (including communication capabilities and on-board diagnostic sensors), machine data is pushed to the cloud, and the data can be accessed through the user interface (HMI). Machine data can be used for predictive maintenance, which means that machine data can be used to estimate when a machine is about to fail.
PLC virtualization here does not refer to the software PLC (SoftPLC) or the software PLC installed in the virtual machine, but refers to the decoupling of the PLC execution environment from the I/O module, and the standardization, modularization and virtualization of the PLC execution environment achieve. The software definition is to abstract the logic of the PLC, and use the software-defined network to realize the program development and management of PLC actions through an application store, allowing the application to define the functions of the hardware PLC. That is to separate the logic control, program storage and IO module of the PLC, and use the application program to realize the logic control part.
When Industrial Internet or Industry 4.0 implements PLC virtualization or software-defined PLC, the following technologies are used:
l Virtualization based on hypervisor or container
l Software Defined Network (SDN)
l Network function virtualization (NFV), etc.
The typical architecture of PLC virtualization is realized in academia and industry. The typical architecture and description are:
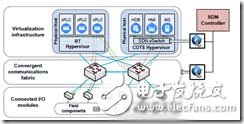
Figure 3 PLC virtualization architecture
In PLC virtualization, the PLC I/O bus is replaced by high-speed network functions. SDN allows flexible virtual channels to be created on the I/O structure to adapt to the connection flow between vPLC instances and I/O modules, such as sensor interfaces Or run the controller, and SDN-based control can provide flexible business isolation. In addition, due to recent advances in field programmable gate array (FPGA) and application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) technologies, this I/O module can be constructed with lower complexity using FPGA or ASIC modules. In this architecture, SDN reconfiguration is managed by the SDN controller via a high-availability (HA) server (not shown in the figure) connected to its northbound. The HA server continuously monitors SDN switch statistics and path reachability, and triggers the reconfiguration process in the event of performance degradation or failure.
The main consideration for the realization of this PLC virtualization architecture is that this distributed model has similarities with remote or distributed I/O PLC topologies, where the network I/O module acts as an extension of the PLC rack. Advances in cut-through switching and remote direct memory access technology (RDMA), especially in the case of converged Ethernet, have allowed the port-to-port delay in the 10G Ethernet switching structure to be reduced to a few hundredths of nanoseconds and applications The delay is reduced to the microsecond level. In addition, resources such as Intel’s Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) and Cisco’s VPP allow the implementation of low-latency, high-throughput packet processing mechanisms that bypass the kernel, bring the network stack into the user space, and enable the adapter to execute directly Memory access operations to application memory. This makes it possible to meet the jitter and flicker requirements of transmission in a unit time of several microseconds, thereby allowing bare metal performance to be realized on commercial server hardware.
The main calculation factors considered in the realization of this PLC virtualization architecture are, first of all, due to the use of hardware-assisted virtualization and other technologies, the server almost utilizes the original performance, low-latency I/O mechanism or ISA expansion suitable for digital signal processing tasks. With increased availability, modern x86 or ARM processors have been able to replace microcontrollers in stand-alone PLC applications. Second, the availability of real-time static partition management programs such as Jailhouse (Siemens), Xtratum, PikeOS, etc. supports the hosting of RTOS client VMs for real-time workloads. That is, in terms of computing, PLC virtualization mainly considers real-time, security and performance requirements. For PLC virtualization, its running real-time static partition management program, considering these characteristics of industrial control systems, its virtualization management program design needs to consider the mixture of several modes at the same time:
1. Fully virtualized mode, in which the operating system runs in a secure partition without modification. In this mode, the hypervisor ensures that the operating system running in it will not damage or affect other operating systems running in parallel in any way, and the operating system running on it can run on the hypervisor without any modification . However, this comes at the expense of a slight performance loss. This mode is mainly used for industrial applications or enterprise applications that have low real-time performance.
2. Para-virtualization mode. In order to ensure the hard real-time performance and stability of real-time code or real-time operating system, the hypervisor also has a deployment mode called "privileged mode or para-virtualization". In the privileged mode or para-virtualized mode, the operating system retains complete hardware access rights and uses the para-virtualized interface provided by the hypervisor. This allows the operating system to run at native speed without the need for the hypervisor to add any delay.
3. That is, in the environment of industrial control system, the virtual hypervisor designed by it must be a hypervirtualized hypervisor with para-virtualization characteristics. Therefore, in the era of the Internet of Things or the Industrial Internet, Xen's inherent advantages have begun to be far ahead of the market. Other virtualization hypervisors.
After reviewing the design of the current industrial control system virtualization management program of foreign manufacturers, the typical situation is mostly the use of a mixture of full virtualization mode and paravirtualization mode. Some examples run monitoring-level functions, while others run hard drives. Real-time control function. Paravirtualization mode or privileged mode does not introduce any delay, so it is suitable for real-time applications. The communication between operating systems is achieved through virtual networks or SDN networks, and shared memory.
The software-defined architecture PLC emphasizes a system and a realization idea. That is, like software-defined networks and software-defined worlds, the embodiment of the intelligence and standardization of PLC equipment is a typical software-defined PLC, including PLCs that are easily connected to the Internet; APP and analysis results are embedded in machines and clouds to realize intelligence and self Awareness; PLC equipment functions can be changed and upgraded without changing PLC hardware, providing users with intelligence and achieving continuous improvement; expanding industrial Internet platform applications through APIs and ecosystems.
A typical implementation architecture is: First, there is an industrial machine that can be used to test the entire production process. This machine can be seen as a set of inputs and outputs that can be controlled through the OT control protocol. This is an ideal real-time protocol because it ensures that messages arrive within a certain time window. Then develop a fog computing or edge computing layer to communicate with the machine during runtime through an industrial control protocol. When it runs, it sends the read data from the machine to the virtual PLC, and then returns the output of the PLC to the machine. As shown in Figure 4 below:
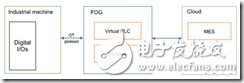
Figure 4 PLC implementation under software-defined architecture
According to the technical scheme tested by this technical framework abroad,

Figure 5 Technical scheme
This technical solution chooses to combine Raspberry Pi with UniPi expansion board to simulate industrial machines. UniPi expansion board provides digital input and relay control for Raspberry Pi. Using CODESYS control software, these inputs and outputs are mapped to Modbus registers and finally passed by the upper layer. Industrial control protocol Modbus to realize industrial control operation. Then at the edge layer or fog computing layer, OpenPLC is used as a logic controller. OpenPLC is a standardized software PLC that can run structured text (ST) programs. OpenPLC includes a Web server, through which our PLC program can be uploaded to the PLC to run. The communication between the simulated industrial machine and the PLC is completed through Modbus. Finally, the PLC needs to be connected to the industrial cloud. This step is to be combined with OpenPLC through the Node-RED tool. Node-RED is a traffic-based IoT tool. It can connect to different devices, APIs and other services. In the edge layer or fog computing layer, the PLC and OPC UA protocol server are connected through Node-RED to realize communication, and the OPC UA client is installed in the cloud to realize the communication between the edge layer or fog computing layer and the cloud.
The edge layer or fog computing layer uses Node-RED as the runtime and OpenPLC as the virtual PLC. Modbus messages can be sent and received using external packets. The input of the machine is read in through the Modbus node and sent to the virtual PLC through another Modbus node. The virtual PLC processes these data and writes the results into its internal Modbus registers. Then Node-RED polls the output of the PLC and sends the result back to the machine. With the help of the OPC UA node, you can send data to the OPC UA server, or you can host your own server during runtime. Then, the IT system or the cloud can access all data in a unified way through this OPC UA protocol.
This is just one of the simplest examples based on the framework, and it is also an example of the final realization. After the virtualization and software definition of the PLC, the decoupling of the lower-level IO will achieve the greatest flexibility and scalability of the industrial control system. In addition, there are many benefits. In the diagram to achieve this, the existing industrial cloud platforms are all running in a mode compatible with the traditional PLC architecture. For example, Siemens’ MindSphere industrial cloud platform, which uses a cloud-based open Internet of Things architecture, can transmit industrial field device data collected by sensors, controllers, and various information systems to the cloud in real time through a secure channel, and Provide enterprises with big data analysis and mining, industrial APP development, and intelligent application value-added services in the cloud. Its architecture is shown in the figure below:
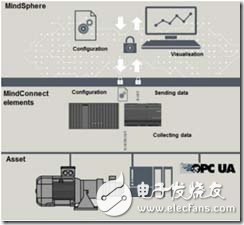
Figure 6 MindSphere industrial cloud platform architecture
The MindSphere platform includes three levels: edge connection layer, development and operation layer, and application service layer. It mainly includes three core elements: MindConnect, MindClound, and MindApps. Among them, MindConnect is responsible for transmitting data to the cloud platform, MindClound provides users with data analysis, application development environment and application development tools, and MindApps provides users with integrated industry experience and data analysis results. Industrial intelligence applications.
In the MindConnect layer, currently the main compatibility is to collect data from an on-site PLC or historical database, directly connect to the PLC or historical database for data collection, or perform data collection through a data acquisition gateway, all operating in a way compatible with the traditional architecture.
This model or technical solution can be called the first stage of the Industrial Internet. To realize the blueprint constructed by the Industrial Internet or Industry 4.0 in the true sense, it is not enough to just collect data for big data analysis, prediction, optimization, etc. We also need the equipment itself to have intelligent computing and intelligent processing capabilities. For the terminal, these optimization and calculation capabilities may be sufficient for the computing capabilities of the smart device itself, but in the real industrial production process, the final control process also needs PLC to control, PLC's intelligent calculation and intelligent processing必须具有软件定义的能力,åªæœ‰é€šè¿‡è½¯ä»¶å®šä¹‰çš„PLC,æ‰èƒ½å¤Ÿé€šè¿‡ä¸Šå±‚çš„æ•°æ®åˆ†æžã€é¢„测和优化之åŽï¼Œæ ¹æ®åº”用功能优化和调整PLC控制程åºï¼Œå®žçŽ°å·¥ä¸šç”Ÿäº§çš„效率æå‡ï¼ŒåŒæ—¶ä¹Ÿé¿å…了人员的ç¹ç调试ç‰ï¼Œæ高è¿è¥æˆæœ¬ã€‚而现有的云平å°è¿˜æ— 法åšåˆ°ç›´è¾¾åº•å±‚çš„ä¼˜åŒ–Ã—Ã—Ã—å®šä¹‰ï¼Œå› æ¤åªæœ‰åœ¨æ‰“é€šå…³é”®æ ¸å¿ƒæŽ§åˆ¶è®¾å¤‡PLCåŽï¼Œæ‰èƒ½å¤Ÿæ‰“通工业互è”网的第二阶段。
工业互è”网ã€å·¥ä¸š4.0ã€ä¸å›½åˆ¶é€ 2025本质都是互è”网深度å‚与到工业生产ä¸ï¼Œä»Žè€Œå°†ç”Ÿäº§åŠ›æå‡åˆ°ä¸€ä¸ªå…¨æ–°çš„高度。过去10年是消费者互è”网的10 年。上一波互è”网浪潮ä¸ï¼Œäº’è”网在全çƒè¿žæŽ¥èµ·æ•°å亿人,åŒæ—¶ä¹Ÿé€ 就了Googleã€äºšé©¬é€Šè¿™æ ·çš„互è”网巨头。互è”网在æµé€šã€æ¶ˆè´¹ã€é›¶å”®ã€æ²Ÿé€šè¡Œä¸šçš„高潮已ç»æœ‰ç›®å…±ç¹ï¼Œäº’è”网在工业生产的领域的浪潮。æ®é€šè®¯å·¨å¤´æ€ç§‘å…¬å¸ä¼°è®¡ï¼Œåˆ°2020年,互è”ç½‘ä¼šé€ å°±150亿至500亿的连接设备,åŒæ—¶è¿˜åŒ…括人与物ã€ç‰©ä¸Žç‰©çš„è¿žæŽ¥ï¼Œæ˜¯ä¼ ç»Ÿäº’è”ç½‘æ—¶ä»£çš„è¿žæŽ¥äººæ•°çš„å‡ å€ç”šè‡³æ›´å¤šã€‚
未æ¥å·²æ¥ï¼Œæ„¿æ—¥ç”Ÿä¸æ®†ã€‚
Bakelite Material,Bakelite Plastic,Bakelite Made From,Bakelite Synthetics
WENZHOU TENGCAI ELECTRIC CO.,LTD , https://www.tengcaielectric.com