Wide bandgap semiconductor gallium nitride (GaN) and related compound semiconductor materials have been widely developed for lighting and various optoelectronic components. The emission wavelength of gallium nitride light-emitting diode (GaN LED) covers the green to deep ultraviolet band. In the foreseeable future, it will completely replace traditional incandescent bulbs and fluorescent lamps as lighting sources.
Another potential optoelectronic component is the Micro Optoelectronic Device (Micro Optoelectronic Device), which is composed of thousands of emitters, detectors, optical switches (OpTIcal Switch) or optical waveguides (OpTIcal) Waveguide) and other micro devices on a single chip. ITRI ​​expects that micro-optical array components will play an important role in the fields of display, biosensor, optical communication or optical fiber communication, optical interconnect (Interconnect) and signal processing (Signal Process) in the future.
Micro LED Array as a display through addressable drive technology, in addition to the characteristics of high efficiency, high brightness, high reliability and fast response time of LED, its self-luminous display-no backlight It has the advantages of energy saving, simple mechanism, small size and thin type. Micro LED has better material stability, long life, no image imprinting, etc. than the self-luminous organic light emitting diode (OLED) display. Its unique high brightness characteristics are used in projection display applications such as micro Projection (Pico ProjecTIon), head-mounted optical see-through display (See-through HMD), head-up display (Head-up Display, HUD), etc., are more competitive. In addition, Nano Second's high-speed response characteristics make LED displays suitable for three-dimensional (3D) display, high-speed modulation, and carrying signals, as a visible light wireless communication function for smart displays.
Micro LED Technology Commission
The surface of the chip of the Micro LED microdisplay must be made into an array structure like an LED display, and each pixel must be addressable and individually driven to light. If it is driven by a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) circuit, it is an active addressing driving structure. The electrical connection between the Micro LED array chip and the CMOS can be formed through packaging technology, such as flip chip bonding. After pasting, Micro LED can improve brightness and contrast by integrating Microlens Array. Figure 1 is a passively addressed Micro LED microdisplay chip. The Micro LED array connects the positive and negative poles of each Micro LED through vertically interleaved positive and negative grid electrodes (P-metal Line & N-metal Line), through the electrode line Turn on the power in sequence, and turn on the Micro LED to display the image by scanning. Active drive displays are more energy-efficient and faster than passive matrix drive methods, and have always been the mainstream drive method for high-resolution displays.

Figure 1 Micro LED passive addressing array architecture diagram and chip photo
Micro LED technology challenges need to be breakthrough
Micro LEDs ("50 microns (μm)) have characteristics that are different from general size (" 100 microns ") LEDs. For example, general-sized LEDs have few problems such as current crowding and thermal accumulation, and may have advantages such as better efficiency due to the release of lattice stress and a larger light-emitting surface. In contrast, a Micro LED with a large surface area may have a large leakage path due to many surface defects. The increase of the series resistance value of the tiny electrode will affect the luminous efficiency. Therefore, the development of micro LED array process and the structural design of micro LED must overcome the above problems. In addition, the uniformity of Micro LED is related to imaging quality and product yield, which is one of the technical development challenges.
In fact, the current Micro LED microdisplays are all single-color, because it is difficult to have epitaxial growth on different wavelengths on a single substrate at the same time, and maintain high-quality LEDs. Therefore, according to the literature, American 3M may convert blue light (or UV) light through the quantum well light excitation layer into red, (blue), and green light by wavelength conversion to form a three-color light mode (RGB) pixel. And Sony (Sony), OKI and other manufacturers tend to adopt the technology of transferring red, blue, and green Micro LED epitaxial thin film in stages (Epi-film Transfer) to form a color Micro LED array. At the micro LED pixel size of about 10 microns, RGB array technology is a technical bottleneck urgently needed by teams around the world.
Progress in technology research and development in various countries
Professor Jiang's team at Texas Tech University published at the end of 2011. So far, the world's most dense (1,693dpi) green light actively addressed Micro LED array chip (Figure 2), up to the video graphics array (VGA ) (640 & TImes; 480) resolution. This microdisplay combines a Micro LED array and a CMOS drive integrated circuit (IC). Each Micro LED has a drive transistor circuit under it, which can control the light emission individually.

Figure 2 Actively-addressed microcrystalline LED array microdisplay developed by Texas Tech University
By optimizing the lithography and etching technology in the semiconductor manufacturing process (Figure 3), the US company Ostendo Technology achieved a Micro LED array with a uniformity of 98% and a density of up to 2,450 dpi on a 4-inch LED wafer. The development of this technology contributes to the practical use of high-resolution LED microdisplays. Ostendo will also use this technology to make a laser diode (LD) array as a projection display source, which will have better optical efficiency than LED microdisplays in projection applications.
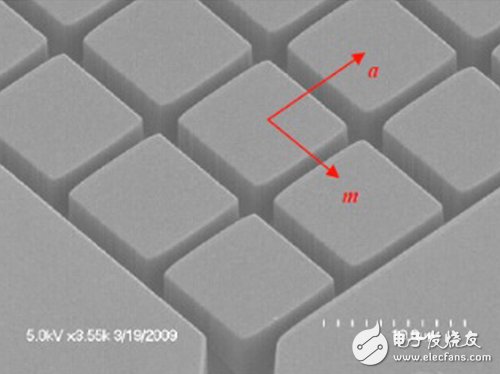
Figure 3 Ostendo Technology's development of Micro LED array process technology with a 10μm pitch
Professor Dawson of Strathclyde University in the United Kingdom has invested a lot in the research of Micro LED. Figure 4 shows the 64 × 64 microdisplay produced by him. They integrated the microlens (Microlens) integrated circuit into the Micro LED array to increase the brightness of the display. In mid-2010, the research team further established the mLED company to provide a Micro LED technology platform to cooperate with customers to develop related application modules or products such as medical, micro display, printing, and semiconductor process light sources.

Figure 4 64 × 64 Micro LED array developed by mLED
Figure 5 is a 240 × 160 Micro LED device produced by the Institute of Industrial Technology. The element size is 7.4 millimeters (mm) x 4.9 millimeters, and the pixel pitch of the Micro LED is 30 microns (846dpi). The Institute of Electro-Optical Science and Technology of the Industrial Technology Research Institute has produced micro LED arrays of red, blue, and green light, and is developing integrated micro-LEDs of red, blue, and green light in a single chip to realize a single chip Micro LED full-color display chip.

Figure 5 240 × 160 blue LED microchip array image produced by the Institute of Industrial Technology
Tsvape is the Chinese supplier of GEEK BAR. We do wholesale business,we sent them from China. Geekbar is an senior e-cigarette brand. It has a high reputation in the world. You can order it with confidence.




Geek Bar Vape,Vape Qd42-V2 4000 Puffs ,Elr Iget Hqd Elrbar ,Elr Iget High-Powe
TSVAPE Wholesale/OEM/ODM , https://www.tsecigarette.com