A few months ago, we introduced our new D24V5Fx buck (step-down) voltage regulator family with inaugural members offering fixed output voltages of 3.3Â V, 5Â V, 9Â V, and 12Â V, and now we have expanded that family by adding versions with fixed output voltages of 1.8Â V, 2.5Â V, 6Â V, and 15Â V.
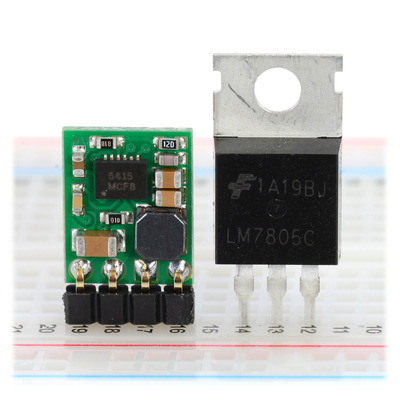
We are particularly excited about this regulator family because of its wide operating voltage range, high efficiencies, and low dropout voltages, all in a compact 0.5″ × 0.4″ × 0.1″ (13 mm × 10 mm × 3 mm) form factor that is smaller than standard through hole linear regulators with DIP packages. For example, the picture below shows a D24V5Fx next to a 7805 voltage regulator in a TO-220 package:
 |
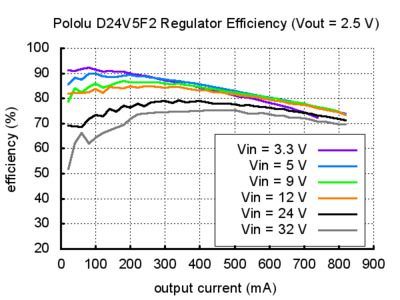
These regulators operate at up to 36Â V, making them especially useful in applications where there can be large variation in the input voltage, such as solar-powered systems or devices where power supply flexibility is a benefit. Since they are switching regulators, the efficiency is much higher than linear regulators when there is a big difference between the input and output voltage, and since they are synchronous, the efficiency is high even at light loads and low output voltages. As an example of the versatility of these regulators, the same D24V5F2 module can in one application be used to get 2.5Â V from a 24Â V battery and in another be an efficient way to add a 2.5Â V node to a system that already has regulated 5Â V. As the performance graph below shows, typical efficiency in the latter scenario is 90%, which could almost double battery life in portable systems when compared to linear regulators.
 |
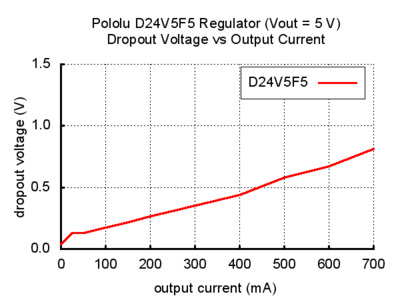
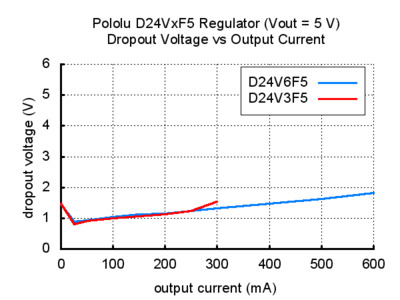
We consider the new D24V5Fx regulators to be next-generation alternatives to our D24V3Fx and D24V6Fx buck regulators, which have been some of our most popular products. In addition to having generally higher efficiencies (which in practice allow these 500 mA units to achieve maximum output currents comparable to our 600 mA D24V6Fx units), these new regulators have much lower dropout voltages (“dropout voltage†is the amount by which the input voltage must exceed the output voltage in order to ensure that the target output can be achieved). For example, the two graphs below show the dropout voltage of the new 5 V D24V5F5 compared to the older 5 V D24V6F5 and D24V3F5:
 |
 |
What this means for your project is broader operating ranges and longer battery life. For instance, a low-power 5Â V system running on a 9Â V battery can discharge it all the way to 5Â V whereas the higher-dropout D24V6F5 regulator can only go to 6.5Â V, and four-cell alkaline and five-cell NiMH packs (both with 6.0Â V nominal voltages) become viable options.
For other regulator options, you can take a look at our full selection of step-up voltage regulators, step-down voltage regulators, and step-up/step-down voltage regulators.
Overhead Line Fitting,Short Insulator Pin For Insulator Supporting,Spindle For Insulator,Ceramic Pin Insulator
Shahe Yipeng Import and Export trading Co., LTD , https://www.yppolelinehardware.com


