In an object system that only works by gravity or elasticity (or is not subjected to other external forces), the kinetic energy and potential energy of the object system (including gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy) are mutually transformed, but the total energy of the mechanical energy remains unchanged. This law is called the law of conservation of mechanical energy.
The law of conservation of mechanical energy (lawofconservation of mechanical energy) is the basic law in dynamics, that is, any object system. If there is no external force to do work, and there is only conservative force (see potential energy) in the system, the mechanical energy (sum of kinetic energy and potential energy) of the system remains unchanged. The external force does zero work, indicating that no mechanical work is input from the outside; only conservative forces do work, that is, only the conversion of kinetic energy and potential energy, and no mechanical energy is converted into other energy. The conservation of mechanical energy in accordance with these two conditions is true for all inertial reference systems. The simplified statement of this law is that when the particle (or particle system) moves in the potential field, the sum of the kinetic energy and the potential energy remains unchanged; or the sum of the kinetic energy and the potential energy does not change when the object moves in the gravity field. This statement implicitly ignores changes in the kinetic energy of objects that produce a field of force, such as the Earth. This can only be established in some special inertial reference systems such as the Earth Reference System. As shown in the figure, if all resistance and energy loss are not considered, the rolling is only affected by gravity. In this ideal case, the gravitational potential energy and the kinetic energy are mutually converted, and the mechanical energy is unchanged, and the rolling will continue to move up and down.
Conservation of mechanical energyThe conservation of mechanical energy is: only the work done by the elastic force or gravity in the system. [Ignore the energy loss caused by friction, so the conservation of mechanical energy is also an ideal physical model], and it is the conservation of mechanical energy in the system. Generally speaking, many mechanical energy is not conserved, but energy conservation can be used, for example, to recover lost energy.
From the WF outer = â–³ E machine in the functional relationship, it can be known that the more general mechanical energy conservation condition is that the work done by the force outside the system is zero.
When the sum of the system's external force or external force is zero, the total momentum of the system remains unchanged, called the law of conservation of momentum.
When only kinetic energy and potential energy (including gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy) are converted into each other, mechanical energy is conserved.
Conservation of mechanical energy three expressions 1. From the perspective of conservation of energySelect a plane to be a zero potential energy surface, and the mechanical energy at the end state of the system is equal to the mechanical energy of the initial state.
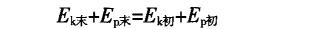
When the kinetic energy and potential energy of the system are mutually transformed, if the reduction of the potential energy of the system is equal to the increase of the kinetic energy of the system, the mechanical energy of the system is conserved.
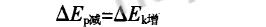
There are A, two objects or more objects in the system. If the reduction of mechanical energy of A is equal to the increase of mechanical energy, the mechanical energy of the system is conserved.
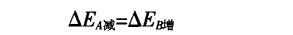
The above three expressions have their own characteristics. In different situations, you should choose the appropriate expression to use flexibly. Don't stick to one kind, so that the problem can be solved simply and quickly.
Typical example analysisExample 1 As shown in the figure, the balls A, B, and C of mass m are connected by two light ropes of length L, placed on a smooth horizontal surface with high h, L "h, A ball just crossed. At the table, if the A ball and the B ball fall to the ground, they will not rebound any more, and ask for the speed of the C ball just leaving the table.
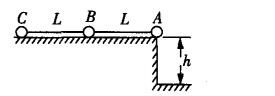
Idea 1: Take the ground to zero potential energy surface,
Let the A ball fall at a rate of v1. During the process from the A ball to the landing, the mechanical energy of the system consisting of B and C balls is conserved.
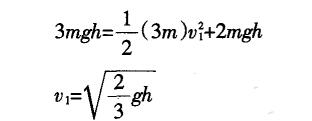
The rate of the B ball landing is %. From the landing of the A ball to the landing of the B ball, the mechanical energy of the system consisting of two balls B and c is conserved.
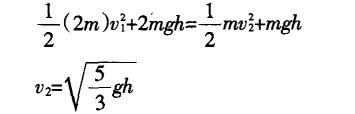
This speed is the speed at which the C ball leaves the table.
This is from the perspective of conservation, respectively, to write the kinetic energy and potential energy of the system's first and last state, and then solve the equations. This kind of thinking is clear and simple, and it is easy to understand. It is necessary to pay attention to the energy to be clarified one by one. .
Idea 2: During the process of landing the A ball, the potential energy of the system is reduced, and the kinetic energy of the system is increased. 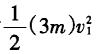
Obtained by the law of conservation of mechanical energy:
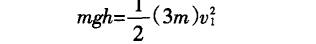
During the process of landing the sun, the system reduces the potential energy mgh, and the system's increased kinetic energy is 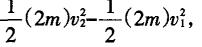
Obtained by the law of conservation of mechanical energy:
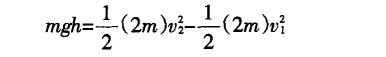
This is from the perspective of the transformation of potential energy and kinetic energy, and the idea is also very clear. It should be noted that the reduction of potential energy or the increase of kinetic energy is systematic, not an object.
Summary of the law of conservation of mechanical energyWork: W=FS·COSï±ï± is the angle between force and displacement
Gravity work: GW=mgΔhΔh is the height difference between the beginning and the end of the object
Gravitational potential energy: pE=mghh is the height of the object's center of gravity relative to the zero potential plane
The relationship between gravity work and gravity potential energy change: GW=-ΔpE is the opposite of gravity work and gravity potential energy
Elastic potential energy: 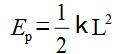 , L is the shape variable of the spring
, L is the shape variable of the spring
The relationship between elastic work and elastic potential energy: FW=-ΔpE is the opposite of the change in elastic work energy and elastic potential energy
Kinetic energy theorem: 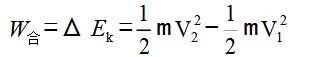 , that is, the external force is equal to the amount of change in kinetic energy.
, that is, the external force is equal to the amount of change in kinetic energy.
Two ways to solve the problem of external force work: 1) First find the external force F, then find the F·S·COSï±
2) First ask each component to do the work and then sum, W1+W2+W3. . . . . .
The law of conservation of mechanical energy: Condition: only gravity elastic work
Formula: E initial = E end, the initial total mechanical energy is equal to the final mechanical energy
Deformation formula: ΔEk=-ΔEp, that is, the amount of change in kinetic energy is opposite to the change in potential energy
If it is the mechanical energy conservation of A and B:
1) 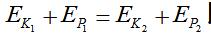 The initial total mechanical energy is equal to the total mechanical energy at the end.
The initial total mechanical energy is equal to the total mechanical energy at the end.
2) 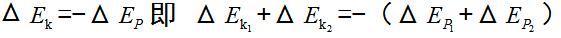 That is, the amount of change in total kinetic energy is opposite to the amount of change in total potential energy.
That is, the amount of change in total kinetic energy is opposite to the amount of change in total potential energy.
3) 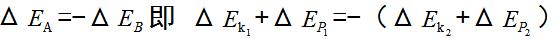 That is, the total mechanical energy change of A is opposite to the total mechanical energy of B.
That is, the total mechanical energy change of A is opposite to the total mechanical energy of B.
Law of conservation of energy: E at the beginning = E at the end, that is, the total energy at the beginning is equal to the total energy at the end.
The situation of mechanical energy changes:
1) W=ΔE machine, that is, the amount of work other than gravity and the internal force of the system is the amount of mechanical energy change (that is, other forces give energy to the original system or consume the original system energy)
2) Friction work affects mechanical energy: that is, the friction multiplied by the relative displacement is equal to the generated heat (internal energy), that is, the loss of mechanical energy.
Blue light filter-using blue light filter technology can eliminate blue light on the phone screen, thereby reducing eye fatigue and fatigue. And keep your eyes healthy and avoid staring at the screen.
Ultra-transparent and protective Ultra-high-quality Ultra HD provides you with clear viewing effects. Let you fully enjoy the super retina display of the screen.
Evacuation Waterproof and Waterproof-The hydrophobic and loose oil transparent layer is used as the final coating to protect screen fingerprints, liquid residues and other stains, keeping your phone in its original condition all day long.
The 0.14mm high-sensitivity touch Ultra-Thin Protective Film can provide real touch and high sensitivity, ensuring that the original high-response touch is not disturbed.
If you want to know more about Anti-Blue Light Screen Protector products, please click the product details to view the parameters, models, pictures, prices and other information about Anti-Blue Light Screen Protector.
Whether you are a group or an individual, we will try our best to provide you with accurate and comprehensive information about the Anti-Blue Light Screen Protector!
Anti-blue Screen Protector, Anti-blue Light Protective Film, Anti-blue Light Screen Protector,Anti Blue Light Screen Protector,Blue Light Blocking Screen Protector
Shenzhen Jianjiantong Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jjthydrogelprotector.com