1. Op amp oscillation two conditions
1. The loop gain is greater than 1 (|AF|>1)
2. The phase difference between the signals before and after feedback is above 360 ​​degrees, and the additional phase is above 180 (due to negative feedback to the reverse end).

A (open loop gain) = Xo/Xi
F (feedback coefficient) = Xf / Xo
2. Operational vibration oscillation judgment method:
Commonly used is the phase margin, that is, when 20lg|AF|=0, the phase offset exceeds 180
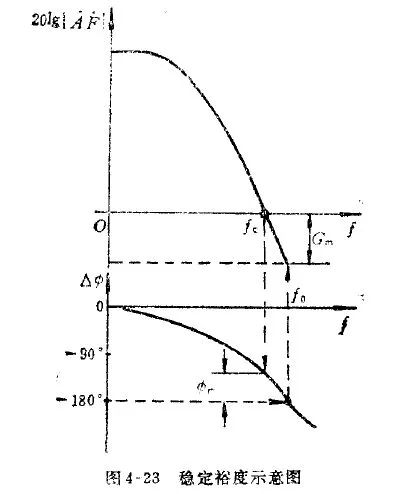
3. Eliminate self-excited methods:
From the self-excited oscillation conditions, the elimination of shock can be started from two aspects:
(1) Reduce the loop gain (but this method increases the op amp gain error)
For the op amp, the feedback coefficient F is reduced. In other words, the larger the F, the more likely it is that the self-excited oscillation will occur. For a resistive feedback network, the maximum value of F is 1, and the typical circuit with F=1 is the voltage follower circuit. This is why the voltage-following op amp is easy to oscillate (this is why we often see the op amp manual marked with unity gain stability, but the gain error of the voltage following is small).
This is also the case for voltage feedback that the capacitive load drive capability increases proportionally with the closed loop gain. Therefore, if the closed-loop gain is 1, the VFA can stably drive a 100pF capacitive load, and if the closed-loop gain is 10, it can drive a 1000pF capacitive load.
However, due to design reasons, the size of the closed-loop gain is usually not changeable, so the applicability of the method is not strong.
(two) increase the phase margin
Phase compensation:
According to the compensation principle, the lag compensation, the lead compensation and the lag-advance compensation
Hysteresis compensation: Any compensation that makes the phase shift lag is called lag compensation. Hysteresis compensation reduces the main pole frequency, ie the amplifier band is narrowed. (similar to RC low-pass filtering)---------- curve 2
Leading compensation: Any compensation that makes the phase shift advance is called advance compensation. The advance compensation makes the amplitude frequency characteristic curve appear zero point, that is, the amplifier frequency band is widened (similar to RC high-pass filtering)-----curve 3
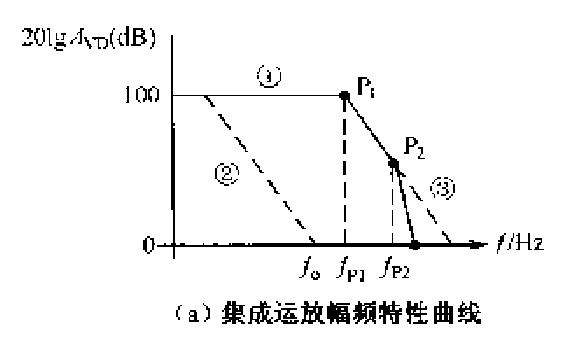
For the capacitive presence (CL) of the load, the loop gain is reduced by the output resistance and CL. At the same time, there is no longer a proportional relationship between phase and gain, and phase lag becomes a decisive factor.
1. Out-of-loop compensation--advance compensation (for small capacitive load <1500pf or load impedance)
A resistor RX is connected in series between the output of the op amp and the load capacitor. Generally, its resistance is 10-100 ohms.


2. In-loop compensation--advance compensation (for large capacitive load >1500pf or load impedance uncertainty)
Rx is within the op amp feedback loop, and a feedback capacitor is connected in parallel with the feedback resistor (this capacitor can eliminate the op amp input capacitance and stray capacitance forming pole). Generally speaking, Rx=50~200Ω, Cf is about 3~ 10pF

Semiconductor Parts
Semiconductor Parts
YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD. , https://www.pst-thyristor.com