
[Netease Smart News August 20 news] Mars 2020 is an ambitious plan. NASA plans to collect 20 Martian cores and soil samples using 1.25 Martian years, or 28 Earth Months. Without artificial intelligence, this task cannot be completed because the probes will waste too much time waiting for instructions.
Currently, the Mars Science Lab team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory plans the daily activities of the Curiosity Mars Rover, and then it takes about eight hours to send instructions through NASA's Deep Space Network. The project leader will tell the rover when it is time to get up, how long it will take to warm up its instruments, and how to avoid rocks that would damage its worn-out wheels.
Mars 2020 will need more autonomy. The person in charge of the Mars Science Laboratory, the task manager of the Mars Science Laboratory, said: “The mission is to progress according to the ground loop.†“The more it can do on its own, the better it can be done.â€
Beyond Never HAL
The $2.4 billion Mars 2020 mission is just one example of NASA's increasing need for artificial intelligence, although the term itself is disturbing to some. Many NASA scientists and engineers prefer to call it machine learning rather than artificial intelligence. In the space domain, this broad term is sometimes reminiscent of Arthur C. Clarke's fictional computer HAL9000 in 2001 "A Space Odyssey", which claims to have perfect records and never make mistakes.

It should be noted that NASA is not trying to create a HAL. Engineers are developing software and algorithms to meet the specific requirements of the mission.
Kelly Fong, senior scientist in the field of automated systems at NASA Ames Research Center and head of the intelligent robot team, said: “The focus of our work today is not on intelligence, but on trying to make the system more independent and automatic. More autonomous."
For manned spaceflight, it is to provide astronauts with software to help them cope with emergencies such as equipment failures and emergency medical care. For example, a medical aid that combines data mining with reasoning and learning algorithms to help astronauts perform multiple missions on Mars and handle everything from daily care to illness or injury – “No need to follow Many flight controllers negotiate," Fong said.
Through robotic exploration of Mars missions, NASA is demonstrating its increasingly powerful detectors. When NASA's Mars Rover Spirit and Opportunity landed on Mars in 2004, they were able to do a very limited job despite their ability to acquire a certain degree of autonomy through software upgrades. In contrast, the ability of Curiosity is obviously much stronger.
Last year, Curiosity began using a software called "Scientific Knowledge Collection and Autonomous Exploration" to combine computer vision with machine learning and select rock and soil samples for research based on criteria established by scientists. The rover can use the laser of its chemical camera to shoot the target, analyze the burning gas, package the image and data, and send it back to Earth.
“The scientists responsible for this task were excited about this because in the past they had to look at the images, pick the targets, send orders and wait for the data to return,†said Kiril Wagstad, researcher of the JPL’s Machine Learning and Instrument Autonomous Group. Said.
Although it takes only 10 to 30 minutes for the data to be transmitted back to Earth from Mars, mission controllers can only use their allocated time within the deep space network to send and receive data.
"Even if the detector can talk to us all day, we can't answer it all the time, can we?" said Wagstaff. “We listened to it only twice a day, once every 10 minutes, because the Deep Space Network was busy receiving contact signals for the Cassini, Voyager, Pioneer, New Horizons and all other missions. ."
The goal of the detector design of the Mars 2020 program is to do more things on its own to better communicate with task managers. It will wake itself up and heat the instrument to the proper temperature before processing the tasks sent to it, and if there is electricity remaining and doing something else.
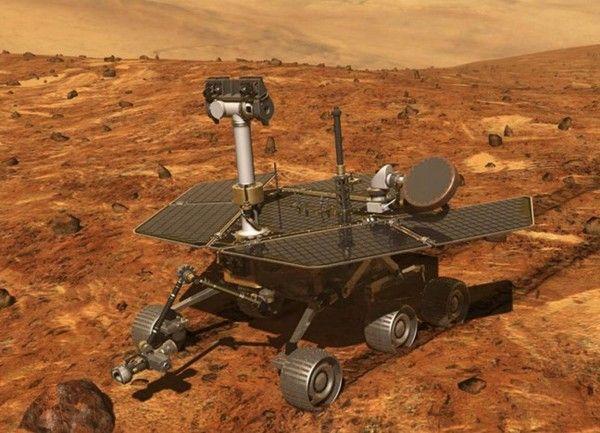

"Ideally, this is good for us. What we want is the image of the target and the data from the instrument. After we have collected these, we will contact us again, and then we will use this information to guide it to obtain a sample." Roseper said.
NASA has not yet achieved this goal, but the Mars 2020 plan has prompted them to improve the software in this direction so that the probe can move from one point to another on the surface of Mars while avoiding obstacles. “It's like the basic skills that toddlers learn and don't bump into obstacles,†he said. This autonomy is increasingly being added to our space program. Looking into the future, I think we will use these smart technologies more and more.
Future missions, such as NASA's Europa Clipper, will require more powerful artificial intelligence to look for plumes rising from the subsurface ocean, as well as cracks on the surface of the lunar ice caused by hydrothermal vents. When scientists cannot predict when or where they will find new discoveries, they will need artificial intelligence to “observe, notice, collect, and send data back,†says Wagstaff.
With the completion of instrument data collection on the Europa spacecraft, the spacecraft's on-board processor needs to “give priority to the observations and send the most interesting data back to Earth.†“We collected more data than we transmitted. ."
This is especially true in missions that are farther from Mars and require satellites for data transfer. Due to the distance, missions to satellite Europa or Saturn will also have communication delays.
NASA has developed software for Earth observation satellites that can be used for ocean observation missions. The "Smart Payload Experiment" satellite launched in 2013 relied on machine learning to analyze images and focused on observations in areas different from the surrounding environment.
"It widens its eyes and looks for anything that we don't anticipate or make a difference with," he said. "We can't predict what we can find. We don't want to miss something because we don't have the skills of a church machine to find things."
One of the future tasks is to survey the existence of life underwater through the ice on the surface of Europa, which will require more machine intelligence. NASA may design software to look for inconsistencies in chemical composition or temperature changes. "It will make you not have to tell it what life is like, what it will eat, and what its energy source is," said Wagstaff.
Before engineers send hardware and software into space, they conduct extensive tests in similar environments on Earth. Engineers test Mars missions in the desert. The best simulation site for the Europa mission may be Arctic glaciers.
"We are acutely aware of the need to reduce risk because it is a spaceship that costs hundreds of millions or even billions of dollars," he said. "Everything we do is sent to the spacecraft after many years of detailed testing."
Artificial intelligence controls everything
The space capsules that SpaceX and Boeing are constructing to and from Earth and the International Space Station are designed to operate autonomously once completed and complete the tasks of docking and returning to Earth.
"This way NASA staff will spend more time learning spacecraft handling than microgravity experiments and keeping satellite orbits shorter." said Chris Ferguson, head of the Boeing CST-100 interplanetary program. And task executives.
"This will greatly reduce the training time. They only need to learn the important things, and how to find the spacecraft did not complete the action according to plan." Ferguson told Space News.
The crew of the interplanetary flight will conduct relevant training on the progress monitoring of the spacecraft. If something goes wrong, they will know how to control it manually and work with ground staff to solve the problem. He added.
NASA insists that part of the reason for achieving a high degree of autonomy is to ensure that space capsules can be used as lifeboats to prevent emergencies.
Ferguson said: "In the event of an emergency, the crew members need to return as soon as possible. They can enter the space capsule without any preparation, close the door, perform a series of actions and return quickly."
In many ways, the spacecraft’s autonomy is similar to that of an aircraft. Whether on a commercial aircraft or a spacecraft, "Everyone is beginning to realize that pilots are increasingly becoming monitors rather than active participants," Ferguson said.
When the spacecraft's spacecraft docks with the space station, the crew will be monitoring complex sensors and image processors. Boeing relies on cameras, infrared imagers and laser detection and distance sensors to create three-dimensional images. The central processor will decide which sensor is more likely to be accurate, and will weight the data accordingly to ensure that the two spacecraft that previously moved quickly eventually complete the docking at a relative speed of approximately 4 centimeters per second.
Although this is a very complicated process, in fact the astronaut sees a similar display with the pilot on the landing system, Ferguson said. (From: SpaceNews çŠ é«¡æ’¸ç®§ebra燱erner Compilation: NetEase Unofficial Smart Compilation Platform çŠç¬® # 貉钤 î î î ?/p>
Pay attention to NetEase smart public number (smartman163), get the latest report of artificial intelligence industry.
ZGAR Aurora 3000 Puffs
ZGAR electronic cigarette uses high-tech R&D, food grade disposable pod device and high-quality raw material. All package designs are Original IP. Our designer team is from Hong Kong. We have very high requirements for product quality, flavors taste and packaging design. The E-liquid is imported, materials are food grade, and assembly plant is medical-grade dust-free workshops.
Our products include disposable e-cigarettes, rechargeable e-cigarettes, rechargreable disposable vape pen, and various of flavors of cigarette cartridges. From 600puffs to 5000puffs, ZGAR bar Disposable offer high-tech R&D, E-cigarette improves battery capacity, We offer various of flavors and support customization. And printing designs can be customized. We have our own professional team and competitive quotations for any OEM or ODM works.
We supply OEM rechargeable disposable vape pen,OEM disposable electronic cigarette,ODM disposable vape pen,ODM disposable electronic cigarette,OEM/ODM vape pen e-cigarette,OEM/ODM atomizer device.

Aurora 3000 Puffs,ZGAR Aurora 3000 Puffs Pod System Vape,ZGAR Aurora 3000 Puffs Pos Systems Touch Screen,ZGAR Aurora 3000 Puffs Disposable Vape Pod System,3000Puffs Pod Vape System
ZGAR INTERNATIONAL(HK)CO., LIMITED , https://www.zgarpods.com