The Internet of Things, the connection of objects and the rapid development of wireless technology provide technical support for the interoperability of information between objects. In the process of the popularity of the Internet of Things, wireless technology will play an increasingly important role. This paper explores the characteristics and application scenarios of wireless technologies under the general trend of the Internet of Things through the comparison of several common LPWAN wireless communication technologies (NB-IoT/eMTC/LoRa).

NB-IoT
NB-IOT is called Narrow Band-Internet of Things, a narrowband Internet of Things, and NB-IOT is a technology in the Internet of Things. It is led by Huawei and has become the LPWA technology of the 3GPP standard.

Based on the existing cellular network technology, NB-IOT can quickly support the industry market demand by upgrading the existing network, becoming the fourth mode on the GUL network. At the same time, NB-IOT also has four capabilities: wide coverage (covering underground), long battery life (more than ten years), low cost (less than $5 per module), and large capacity (single cell can support 100,000 connections). .
Technical advantages
NB-IoT has four characteristics: First, wide coverage will provide improved indoor coverage. In the same frequency band, NB-IoT gains 20dB more than the existing network, which is equivalent to the ability to increase the coverage area by 100 times.
Second, it has the ability to support massive connections. NB-IoT can support 100,000 connections in one sector, supporting low latency sensitivity, ultra-low device cost, low device power consumption and optimized network architecture.
Third, lower power consumption, NB-IoT terminal module standby time can be up to 10 years;
Fourth, the lower module cost, the company expects a single connected module to not exceed $5.
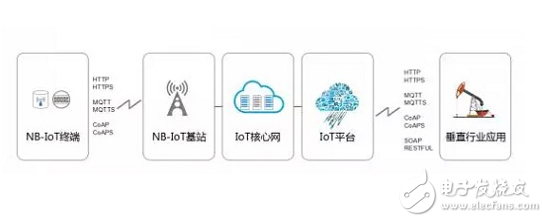
Focusing on the Low Power Wide Coverage (LPWA) Internet of Things (IoT) market, NB-IOT is an emerging technology that can be used globally. It has the characteristics of wide coverage, many connections, low speed, low cost, low power consumption and excellent architecture. The NB-IOT uses the license band and can be deployed in the inband, guard band or independent carrier mode to coexist with the existing network.
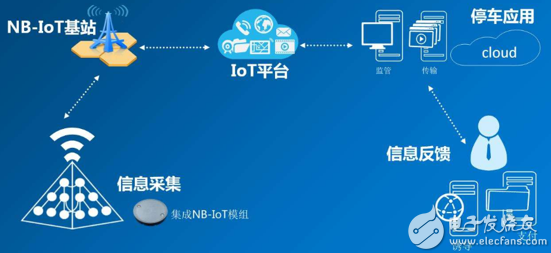
Application scenario
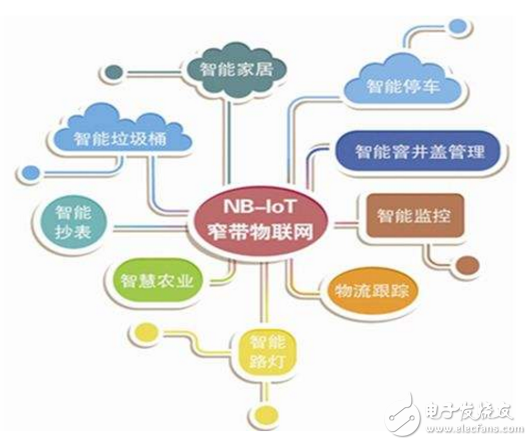
NB-IOT is most commonly used in three typical application scenarios of smart water meter, intelligent parking and pet intelligent tracking. In the later planning of NB-IOT, it will also involve smart bicycles, smart smoke detectors, smart trash cans, intelligent roads, Intelligent vending machines and other aspects.
The challenge is first, interoperability and consistency issues. In 2015, key members of NB-IoT, including Vodafone, Ericsson, Telefonica and GSMA, conducted simple interoperability and conformance certification tests for NB-IoT devices. Vodafone also established a dedicated NB-IoT laboratory in Newbury, England, and continued to open further laboratory research in Düsseldorf, Germany in the second half of 2016.
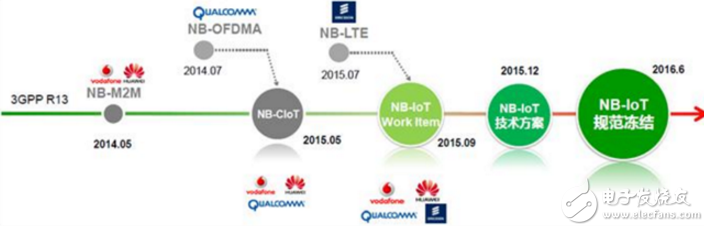
(NB-IoT protocol formation process)
Second, deployment and long-term support. The biggest problem with NB-IoT deployment is time and cost. According to Vodafone estimates, 85% of enterprise base stations can support NB-IoT, only software upgrades are required, but for network operators with stale base stations, hardware upgrades are required. . This will result in increased cost and time consumption for NB-IoT network construction. Another issue is global M2M roaming. In theory, operators need to support three standards: CAT-M, EC-GSM, NB-IoT, and GPRS. In addition, endpoints require an OTA upgrade to provide security and other upgrades.
Third, applications and business models. In order to build NB-IoT applications and business models, the mobile communications industry needs to establish a partner ecosystem as soon as possible. For example, Deutsche Telekom has established NB-IoT prototype hubs in Berlin and Krakow, Poland. These hubs are included in the incubator, providing developers with a fast learning environment, inspiring new business model thinking and shortening the time to market. .
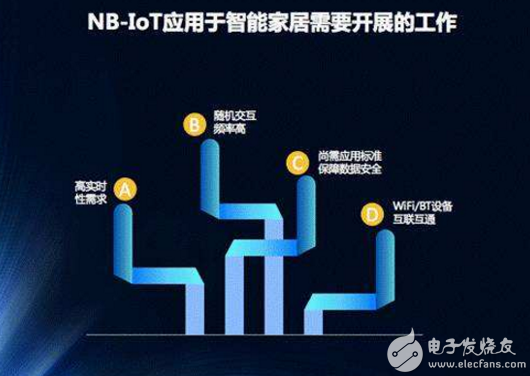
Fourth, competition with LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Internet of Things) technology. LoRa and Sigfox have proven to be important development technologies, with Sigfox already in use in 24 countries and LoRa continues to be used in some countries, private networks and community networks. Since NB-IoT will not be deployed on a large scale in the near future, other technology competitors still have the opportunity to determine their market position.
At present, the market penetration of NB-IoT varies among countries. In many countries, potential operators may face strong competition from non-mobile LPWAN networks. For example, in the Netherlands, KPN has established a national LoRa network, in which case it may not be able to adopt NB-IoT.
Fifth, determine the correct market entry strategy. The application of LPWAN has the feature of transmitting small data payloads in unconventional intervals. Potential users may need more low value services. In this case, NB-IoT operators need to develop strategies to deal with such market demands. The main strategies include: establishing a balance between the market and the brand; expanding market share is not limited to traditional M2M business; avoiding cost price wars in the low-end market, focusing on applications that can control price premiums; exploring new business models to create value, Strengthen vertical industry cooperation.
Sixth, the design of the pricing plan is mainly the IoT data plan. Currently, operators are still trying. For example, Korea Telecom recently launched a nationwide LoRa network, launching six data plans, each of which corresponds to data applications using different frequency bands. Its pricing model is: LoRa's data plan price is only one-tenth of the LTE-based IoT business. In countries with LoRa or Sigfox business, NB-IoT tariffs have to maintain a reasonable competition range. In the UK, because there is no national LPWAN network, NB-IoT operators will have more room for manoeuvre when designing pricing structures.
In addition, low-speed data transmission, privacy and security, and the conversion time of IT systems will limit its development.
eMTC
LTE-M, LTE-Machine-to-Machine, is an Internet of Things technology based on LTE evolution. It is called Low-Cost MTC in R12 and LTE enhanced MTC in R13, ie eMTC. It is based on existing The LTE carrier meets the needs of IoT devices.

The eMTC is deployed on a cellular network and supports a peak rate of up to 1 Mbps for uplink and downlink. It belongs to the Internet of Things. Its user equipment can directly access the existing LTE network by supporting 1.4MHz RF and baseband bandwidth. In the process of continuous evolution of LTE, the latest eMTC and NBIoT further optimize the cost of the system, enhance the endurance and expand the coverage. The most critical capability of eMTC is to support mobility and can be located at a cost of only 25% of the Cat1 chip, which is four times higher than the GPRS rate.
Technical advantages Narrowband LTE is one of the most important features. First, the complexity of the system is greatly reduced, and the complexity and cost are greatly optimized.
Second, the power consumption is extremely reduced, and the battery life is greatly enhanced.
Third, the coverage of the network has been greatly enhanced.
Fourth, the density of network coverage is enhanced.
eMTC has the basic four capabilities of LPWA: First, wide coverage, in the same frequency band, eMTC has 15dB better than the existing network, which greatly enhances the deep coverage capability of LTE network; second, it has the ability to support massive connections, eMTC One sector can support nearly 100,000 connections; third is lower power consumption, eMTC terminal module standby time can be up to 10 years; fourth is lower module cost, large-scale connection will bring module chip cost The rapid decline, the target cost of eMTC chip is about 1 to 2 dollars.
Application scenario

It is used in intelligent logistics, with anti-theft, anti-switching, real-time temperature sensing and locating advantages. It can monitor and locate in real time, record and upload information, and query the driving track. In smart wearable devices, it can support health monitoring. , video services, data backhaul and positioning; relying on the current cellular interactive screen, providing application scenarios including smart charging piles, waiting treasures, elevator guards, intelligent bus stop signs, public bicycle management, etc.
Challenge

Applicability Analysis of eMTC Service Features to VoLTE Services
The typical difference between eMTC and NB-IoT is that the working bandwidth of eMTC terminal can reach 1.08MHz, which is much higher than 200kHz of NB-IoT terminal. Therefore, the peak rate of eMTC terminal is much higher than that of NB-IoT terminal. Based on the above features, the industry generally believes that eMTC technology can provide a relatively low-cost VoLTE terminal solution and can have better service quality. However, through detailed technical analysis, eMTC technology can support voice services or provide voice solutions. The actual effect may be difficult. optimism.
Low-Power Features In order to provide IoT services in a power-constrained environment, like NB-IoT, eMTC also targets low-power consumption as a system design goal. It is expected to support 10-year maintenance-free terminals based on smaller capacity batteries. As with NB-IoT, two power saving technologies, eDRX (Extended Discontinuous Reception) and PSM (Power Saving Mode), are adopted. For typical low-frequency IoT services, such as automatic meter reading, because the frequency of services is very low, these two technologies can make the terminal sleep for a long time, and only work when data transmission is needed, so it can save power. However, this good power saving effect is only effective for the lower frequency service. For the VoLTE service, the terminal needs to frequently listen to the network paging and respond to the incoming call in time, so the power saving mechanism of the eDRX and PSM technologies cannot be adopted. .
The requirements of the Internet connection feature of the large connection feature require the Internet of Things technology to serve a large number of terminals. For this reason, 3GPP has designed two control schemes, CP (Control Plane) optimization and UP (User Plane) optimization, for the IoT service delivered by the packet. It can save a lot of air interface signaling and improve transmission efficiency. However, for the VoLTE voice service, the CP and the UP optimization solution cannot be used to increase the capacity. Therefore, the eMTC does not have the capability of improving the capacity for VoLTE.
The wide coverage feature considers that some IoT terminals are often located in deeper interiors of buildings. Typical water meters, for example, often have very weak signals. eMTC designs repetitive techniques to enhance coverage, and repeats the uplink and downlink wireless signals. Signal energy can be accumulated at the receiving end to enhance coverage. However, due to the repetition of the wireless signal, the average service rate is reduced. That is to say, the coverage enhancement technology is exchanged at the cost of the service rate reduction. Therefore, for a service that requires a certain rate guarantee, such as VoLTE, eMTC The coverage enhancement technology did not bring any benefits.
Low-cost eMTC terminal solution
The low-cost solution of the eMTC terminal (chip) mainly includes: a small working bandwidth, and the working bandwidth of the eMTC terminal is 1.08 MHz. Although the working bandwidth is higher than that of the NB-IoT, it is much lower than that of the ordinary LTE terminal. Lowering device price and chip computing power requirements, thereby lowering overall price; lower peak rate, lower peak rate reduces GPU computing power and Buffer requirements compared to LTE, thereby reducing chip price; single-terminal receive antenna, Reduce the cost of RF devices; half-duplex solution can save the terminal RF transceiver, thus reducing the cost of the terminal.
LoRa

LoRa is one of the LPWAN communication technologies. It is an ultra-long-range wireless transmission scheme based on spread spectrum technology adopted and promoted by Semtech. This solution changes the previous trade-offs between transmission distance and power consumption, providing users with a simple system that can realize long-distance, long battery life and large capacity, and thus expand the sensor network.
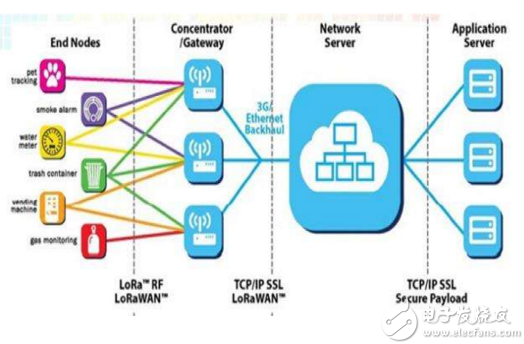
( composed of LoRa network )
Currently, LoRa operates primarily in the global free band, including 433, 868, and 915 MHz. LoRa technology features long range, low power consumption (long battery life), multi-node, and low cost. The LoRa network is mainly composed of a terminal (with built-in LoRa module), a gateway (or base station), a server, and a cloud. Application data can be transmitted in both directions.
Technical advantages on-demand deployment: LoRa can plan and deploy the network according to the needs of the application, and place the base station/gateway according to the on-site environment. It is easier to seamlessly cover, and improving the coverage quality can also reduce power consumption, improve system capacity, and personally. The enterprise or organization can be deployed and can meet security needs, and the data can be private.
Lightweight: Compared to other LPWAN technology protocols, LoRa has lower system complexity, simple hardware implementation, lower resource requirements, and lightweight LoRaWAN protocol. The software is simple to implement and simple to deploy.
Low cost: LoRaWAN module is mass-produced, the price is already below USD5, and it is gradually approaching the price of 2G module. The outdoor base station has been as low as USD500, and the indoor type is USD100. From the perspective of foreign operators, LoRa monthly rent can reach eMTC monthly rent. 1/5~1/10 or even lower.
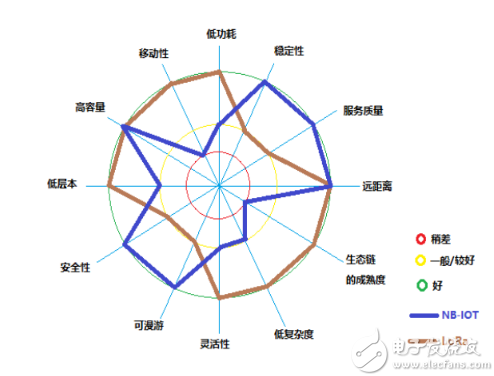
NB-IOT and LORA comparison
Effectively respond to low ARPU: APRU for a single connection is very low, high investment will face low yield problems, high quality, lightweight, low cost is an effective response.
Open ecology, mature industry chain: nodes, gateways and cloud servers are all open, all kinds of equipment are available for selection, the network can operate by itself, different business and operation modes.
The return on investment is high and economically viable: If only the investment of the base station is considered, the return rate of LoRa is that the base station recovers the base station investment at an average of RMB5000 and 6.25 months (half a year). The return rate of NB-IOT is based on comprehensive consideration of base station upgrades and new construction, assuming an average of 150,000 yuan/station and 187.5 months (15.6 years) to recover base station investment.
Application scenario
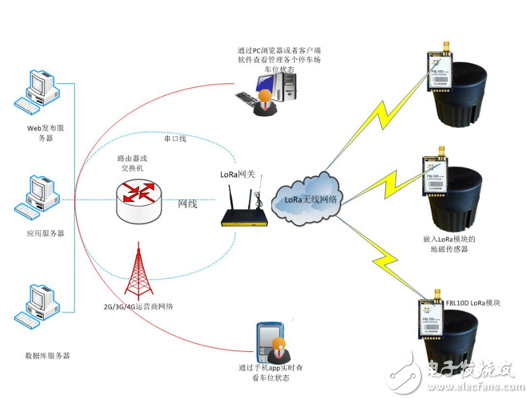
LoRa technology is ideal for IoT applications that require low power consumption, long distances, large numbers of connections, and location tracking, such as smart meter reading, smart parking, vehicle tracking, pet tracking, smart farming, smart industries, smart cities, smart communities, etc. Other applications and areas.
Challenge

City-level network coverage: LoRa has no operator's expenditure, and the network is inherently weak.
Spectrum resources: LoRa uses free frequency bands, which may have interference problems. Although LoRa itself has strong anti-interference ability, LoRaWAN protocol itself has measures to avoid interference. However, physical interference is difficult to avoid completely. Response measures: Defragmentation, construction of a unified WAN network, network building, and resource sharing. At the same time, it needs to be more lightweight and lower cost. The cost of the LoRaWAN module needs to be in line with the cost of the 2G module, even to the WiFi module.
Summary: Each technology has its own characteristics and advantages to meet different demands and markets. Multi-LPWAN technology will bloom and coexist.
Panasonic understands manufacturers` challenges in adapting to the demands of increasingly wider market segments. So Panasonic designed a common platform that incorporates jumper wire and radial solutions in both the high-density and high-speed arenas, and an expanded axial solution with built-in jumper wire flexibility.
Radial Insertion Machine,Universal Radial Insertion Machine,Panasonic Radial Insertion Machine,Panasonic Insertion Machine
Shenzhen Keith Electronic Equipment Co., Ltd. , https://www.aismtks.com