2017 is considered to be the first year of NB-IOT commercial business. Since the core standard was frozen in June 2016, everyone believes that NB-IoT will enter a stage of rapid development. NB-IoT is favored for its massive connectivity, ultra-low power consumption, deep coverage, security, reliability and low cost. Looking at it now, operators and equipment manufacturers are actively promoting the improvement of the entire eco-industrial chain of NB-IoT and promoting the application of downstream applications.

Let's first take a look at the history of NB-IoT development:
1. In 2014, Huawei and Vodafone jointly proposed NB-M2M
2. In May 2015, Huawei and Qualcomm jointly announced a converged solution, namely uplink FDMA multiple access and downlink OFDM multiple access, named NB-CIoT (NarrowBandCellularIoT). 3. On August 10, 2015, at the last meeting of the GERANSI stage, Ericsson and several companies proposed the concept of NB-LTE (NarrowBandLTE).
4. In September 2015, 3GPP reached an agreement in the RAN plenary meeting in September 2015. The two technical solutions of NB-CIoT and NB-LTE were merged to form NB-IoTWID. NB-CIoT evolved to NB-IoT (NarrowBandIoT), establishing NB-IoT as the only standard for narrowband cellular Internet of Things.
5. In April 2016, Huawei announced the establishment of NB-IoT Open Lab with Vodafone at the M2M conference in London.
6. In April 2016, the NB-IoT physical layer standard was frozen in 3GPPR13.
7. In June 2016, the NB-IoT core standard was officially frozen in 3GPPR13.
8. In the first quarter of 2017, according to the “National New Generation Information Technology Industry Planâ€, the NB-IoT network was designated as one of the key projects of the “13th Five-Year Plan†of the information and communication industry.
9. On April 1, 2017, Haier, China Telecom and Huawei signed a strategic cooperation agreement to jointly develop an IoT smart life plan based on the new generation of NB-loT technology.
10. On April 25, 2017, the Global Mobile Communications Equipment Suppliers Association released data. Currently there are only four NB-IoT commercial networks in the world. But at the same time, it is pointed out that 18 operators in at least 13 countries plan to deploy or are testing 40 NB-IoT networks.
11. In May 2017, Softbank will cooperate with Ericsson to fully deploy Cat-M1 and NB-IoT networks in Japan, with a view to launching commercial cellular IoT services in Japan.
12. In May 2017, China Unicom Shanghai announced the completion of commercial deployment of Shanghai NB-IoT at the end of May. In the first half of 2016, Shanghai Unicom built the world's first preNB-IoT large-scale continuous coverage area, Shanghai International Tourism Resort, and jointly launched Huawei's intelligent parking solution for NB-IoT technology.
13. In May 2017, it was revealed that Huawei NB-IoT chip Boudica120 will be shipped in large quantities at the end of June.
From the above materials, we have seen the development history of NB-IoT, and also saw Huawei's leading role in NB-IoT. The first-class enterprises do the standard. This sentence has a role model for Qualcomm and other companies in the communications industry, so Huawei’s intention is obvious. This article will mainly analyze Huawei's strategy on NB-IoT.
The first point to note is that NB-IoT is part of Huawei's entire IoT strategy, so we must start with Huawei's IoT strategy. In the field of Internet of Things, Huawei proposed its "1+2+1 strategy." The first "1" refers to a platform. Huawei wants to establish an IoT platform, collects, manages, and processes data and then opens it to partners and industries. Based on the platform, industry partners can develop applications. "2" means that Huawei's traditional advantage is network access, including wired access and wireless access, such as agile IoT network (IoT gateway, smart home gateway) and eLTE/NB-IOT/5G; the last one "1" is Huawei's new lightweight Internet of Things operating system LiteOS. Therefore, NB-IoT is a platform that is integrated into the entire Huawei Internet of Things system and shares the Internet of Things with other communication technology applications. It is said that Huawei has invested 3,300 R&D personnel in the field of Internet of Things, including: HuaweiLiteOS300, 800 wired access (AR/SmartHGU), and 1,200 wireless access (eLTE/NB-IoT/5G). The IoT management platform is 600 people, the solution is 300 people, and the standard cooperation is 100 people. At the same time, eight R&D centers are established around the world: Munich, Germany (Industry 4.0), Santa Clara, USA (Industrial Internet and IoT standards), London, UK (NB-IoT and IoT solutions), Beijing (Industry 4.0), Wuhan ( Smart Home), Shanghai (NB-IoT); Shenzhen (IoT platform, LiteOS, IoT solution), Nanjing (wired access AR). In addition, in the field of Internet of Things, Huawei focuses on industry applications, including public infrastructure, smart homes, car networking, manufacturing, energy and other vertical industries. To this end, Huawei actively cooperates with various industry brands.

In LPWAN (Low-Power Wide Area Internet of Things), because Huawei is a telecom equipment manufacturer and has a good cooperative relationship with telecom operators, it chooses the cellular technology NB-IoT that authorizes spectrum. In fact, there are technologies such as LoRaWAN, Sigfox, Weightless, HaLow, and RPMA (RandomPhaseMulTIpleAccess) for unlicensed spectrum. LoRa has been commercial for several years, and it is still very attractive to operators in the non-telecom field. The Internet of Things is a market with multiple scenarios, and there should still be room for development in the future.
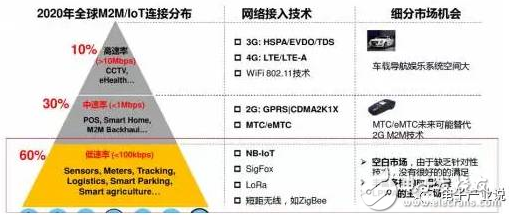
In fact, the real threat to Huawei's NB-IoT development path should be LTE-M (called Low-CostMTC in R12 and LTEenhancedMTC (eMTC) in R13, which aims to satisfy the Internet of Things based on existing LTE carriers. Equipment requirements). Among international operators, AT&T, Verizon, KDDI, KPN, Orange, NTTDoCoMo, Telefonica, Telstra, and Telus have successively launched commercial eMTC. Domestically, China Unicom and Telecom have begun large-scale investment in NB-IoT, but mobile seems to still have some reservations between NB-IoT and eMTC, so there is still some uncertainty in the future. Even TomRebbeck, a director of market research and consulting firm AnalysysMason, analyzed that the price difference between NB-IoT module and LTE-M module is not big, and there is not much difference in battery performance/lifetime between the two. However, the performance of LTE-M is much higher than that of NB-IoT, and compared to NB-IoT, LTE-M will be more flexible for the future development of new applications. Especially in its peak rate, mobility, voice capabilities, it is suitable for IoT applications where medium throughput, mobility or voice capabilities are required.
So if LTE-M becomes mainstream in the future, it is very unfavorable for Huawei. Therefore, for Huawei, it is time to quickly promote the commercialization of NB-IoT, improve the ecosystem of NB-IoT, and popularize NB-IoT as soon as possible. At the same time, in terms of technology evolution, from Rel-13, to Rel-14 support NB-IoT positioning, MulTIcast, enhanced non-anchor PRB, mobility and service continuity, and Rel-15 will support SmallCells and TDD Etc., in order to better support the various application scenarios of the Internet of Things.
From the perspective of the entire industry chain, in order to popularize NB-IoT, it is necessary to open up various chains such as cloud management. The opening of the network here is not only the opening of technology, but also the opening of various interest chains. Different from the high ARPU value of the previous telecommunication broadband service, due to the dispersion of the IOT market, the traffic revenue obtained through the pipeline only accounts for a small part, and more value lies in the application service capability. Although this telecom operator has built various cloud platforms and applications based on the Internet of Things, there should be some distance due to lack of understanding of the application of the industry. Huawei clearly has the incentive to help operators further support their technology. Huawei's products and solutions, MarkeTIng and President of the Solution Department, Zhang Shunmao, said that Huawei can do more than provide Internet of Things connection management platform, and can also do certain industries and Pre-integration of class applications and then providing these pre-integrated vertical industry solutions to operators. This sentence also well illustrates Huawei's positioning in the field of Internet of Things.

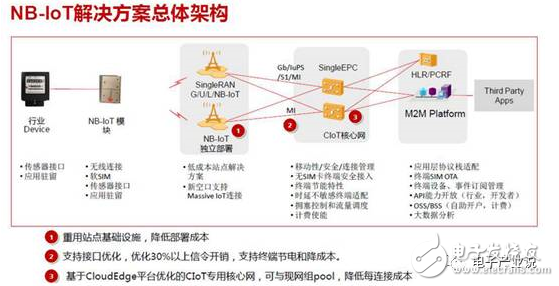
In addition to helping operators, Huawei is also actively working with partners in various industries. Because the entire NB-IoT industry chain includes chip/module manufacturers, terminal equipment manufacturers, network operators, system suppliers, integrators, integrated solution providers, data analysis vendors, service providers, and large-scale development. , small and medium developers, and more.
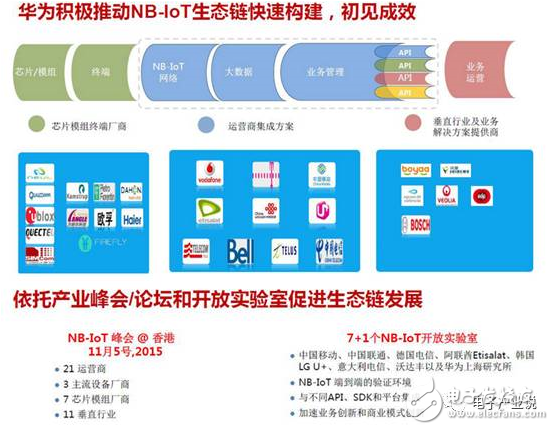
The entire industry can only develop if all parties benefit. To this end, Huawei has maintained an open strategy to cooperate with manufacturers and developers of the entire industry chain. Including cooperation in the establishment of the NB-IoT alliance, the establishment of the Spark Group, and many automakers such as Audi FAW, and cooperation with Honeywell, Haier, etc., and cooperation with Mobai to establish the application of NB-IoT in shared bicycles. At the same time, in order to enable more partners to apply more quickly, for end-to-end NB-IoT development, Huawei provides a variety of open capabilities to help partners quickly develop integration, such as providing SoftRadio for end-to-end basic function debugging. In 2016, Huawei established seven open laboratories around the world, and now two are open, one is Vodafone and the other is Huawei's research institute. The open lab is mainly to build a complete end-to-end NB-IoT environment, providing NB-IoT chips and modules, and some close-knit partners to do end-to-end docking, including chip module integration, after The connection management platform of the end, the docking of the business server, and the like.
For NB-IoT commercial, the first stage is to seek large-scale homogenized terminals, such as water meters, electricity meters, municipal street lights, environmental monitoring, bicycles, etc., because the scene is relatively simple, which is conducive to polishing NB-IoT technology. . However, it is crucial to have a larger scale of popularization and design a good business model to benefit all parties in the interest chain. The first consideration is the cost issue. The cost of NB-IoT in the application field includes hardware cost, network cost, installation cost, and service cost. The first consideration is hardware cost, chip and module cost. According to forecasts, when the module shipment of NB-IoT reaches 10 million, the cost of the module is expected to be close to 2G module, less than 5 US dollars. It is said that Huawei is expected to ship large-scale NB-IoT in June, and the overall hardware cost reduction of NB-IoT is a major positive. In general, subsidies for operator modules are a common method, but this is based on the premise that operators can get excess benefits from traffic operations. It seems that the Internet of Things does not work. The consensus is that only from the vertical application of the platform and applications, from the value of data mining, is the future business model. But how the whole model is designed, how to consider the interests of all parties, including the price design, is a huge challenge. Therefore, if Huawei can work with partners in the entire ecosystem to achieve a true transformation of the business model, it will be of great significance to Huawei and even the entire NB-IoT industry.

Whaylan 80W portable power station
- High conversion efficiency, high-transmission rate.
- Energy saving, environmental-friendly, Safty, No pollution
- Advanced technology, strict quality control system.
- Easy installation, safe operation, free maintenance.
- 10-year product warranty,12-year warranty at 90% power output,25-year warranty at 80% power output
- Quality in priority, clients the upmost.
Foldable Solar Panel,Flexible Solar Panel,Oem Solar Panel,Solar Panel Charger
suzhou whaylan new energy technology co., ltd , https://www.whaylan.com