[Introduction]: In this era, automatic driving has gradually increased the attention of the industry and outside. Although automatic driving is good, there are many problems that need to be solved at this stage. Supervision is an important part. How does China and the United States regulate self-driving cars? What can we do to ensure safety and responsibility?
Tencent Research Institute's "foreign expert face-to-face" series of activities recently invited Professor Robert P. Merges, chairman of the Michigan Autonomous Vehicle Law Association (Autonomous vehicle law associaTIon), to "Autonomous vehicle regulaTIon: US and China Share the theme.
Professor Merges believes that there are three dimensions to the supervision of autonomous vehicles.
The first dimension is safety and responsibility. The multiple layers of supervision in the United States each bring complexity to safety and responsibility issues;
The second dimension is related to vehicle coordination, intellectual property rights, system opening and closing, etc., which has not attracted enough attention at present;
The third dimension is the impact of autonomous driving on employment. Governments and enterprises need to eliminate public panic and cultivate public trust in technology.
Finally, for everyone to discuss the heated ethical issues, Professor Merges believes that this issue will be philosophically unsolvable, but the system designer can continue to improve the safety performance of autonomous driving from avoiding any collision and death, rather than describing it as An advance programming option involving ethics.
1. Generation problem of autonomous driving technology:
Safety and responsibility
1. The three levels of American autonomous driving legislation bring the complexity of legal supervision
California in the United States defined autonomous driving technology in 2012: autonomous driving technology refers to the technology of driving a vehicle without the active control or monitoring of a human driver. The definition can also be used to explain California ’s insurance policy for autonomous vehicles.
So from the beginning, California was often the first state to promote autonomous driving technology and introduce legislation to regulate it. In contrast, Washington State's autonomous driving policy was introduced relatively late, and it has not been so straightforward so far. So far, the level of federal policy is more of some guiding principles, making recommendations to the state legislation.
Therefore, at this level, in the United States, most of the truly binding legislation for autonomous vehicles is at the state level.
Moreover, there are differences in the regulatory systems of the states. For example, many states do not have legislation related to autonomous vehicles. This explains some of the phenomena we may see-why self-driving cars are tested in one state and not in another.
Because the state of self-driving cars in these states is very unclear, there is a lack of legal guidance on what is legal and what is illegal, so operating (operating) self-driving cars is risky. Therefore, research on self-driving cars is often concentrated in some states that have passed relevant laws or regulations.
In addition, after the accident, the laws vary from state to state. For example, when a self-driving car travels from California to Oregon, the legal situation is uncertain, so it is difficult for people to predict.
This brings both challenges and opportunities. Because if the company is going to test self-driving cars in the United States, he can choose to test in the places that are most beneficial to him. This is a positive aspect.
In addition to the national and state levels, there is a third level, that is, legislative supervision at the municipal government level. Normally, the state government is responsible for formulating requirements on liability and insurance, while the municipal government is more responsible for the formulation of road traffic rules and some local rules, such as pedestrian rules, traffic light rules, and special rules, such as Involves bicycle lanes and rules related to disabled people.
Because the supervision of the three levels of government will interact, when there are problems in some places, there will usually be three levels of government to review the accident or problem. This is a characteristic of the American legal system, which creates some complexity.
Some companies, including Waymo, choose to go to Arizona for autonomous driving tests. However, there have recently been pedestrian deaths in Arizona due to self-driving car traffic accidents. Therefore, it can be expected that this will cause a lot of attention.
Sometimes the occurrence of accidents may lead to the shelving of legislation and technology promotion. For example, sometimes the state government will suspend the test of self-driving cars until the situation and cause of the accident are studied. In the United States, because the authority to supervise accidents and liabilities belongs to the state government, it is difficult to accumulate the necessary knowledge base to compare the safety performance of autonomous vehicles with traditional vehicles.
As most people should know, the “Gold Standard†has so far been the long-term average of traditional driving mortality. Therefore, in the US safety plan, our goal is to develop sufficient data to compare the safety performance of autonomous vehicles and traditional vehicles. However, because the accident rate of self-driving cars is very low, the accumulated data is relatively small, and because of the great differences in the self-driving systems so far, our research is still in its infancy.
In the United States, Arizona tracks the mileage of self-driving cars in that state, as do other states such as California, New York, and Washington. We need to coordinate the safety data of each state, so it is necessary to establish a national database to compare the traditional "gold standard" of human driving with the mortality rate of autonomous vehicles.
However, through the understanding of the US regulatory system, it is difficult to compare safety data among all states if regulation is performed at the state level. So the challenge facing the federal system is coordination between states.
2. Responding to autonomous driving accidents: thinking like a psychologist, not thinking like an engineer
To be sure, the mortality rate of self-driving cars will be more conspicuous and will attract more attention. Therefore, any regulatory policy and corporate response should take into account the fact that self-driving technology is a new technology for ordinary consumers, which means that they may feel a little fear, and the media may magnify it.
Therefore, the response to accidents, especially fatal accidents, must take into account this fear of consumers. Although overall, the accident rate of self-driving cars is much lower than that of traditional cars, the accidents of self-driving cars will cause people's special attention. Therefore, self-driving car companies must be very sensitive to consumer reactions.
As a technician, we often analyze each accident and think about how to prevent it. But in order to maintain public relations and increase consumer acceptance, the response to negative events is very important, because this new technology is often more terrible for people. So we need to think like a psychologist, not an engineer.
3. Federal regulation rules for autonomous vehicles
Next is the US federal regulation rules, which is the most similar to China in the US regulatory structure, because the federal government regulates through top-down directives.
The US federal government is mainly responsible for the formulation of safety standards, while leaving other regulatory responsibilities to the state government. The state government retains its traditional responsibilities, such as the issuance and registration of vehicle licenses, the formulation and enforcement of traffic regulations, and the formulation of insurance and liability frameworks. As part of the Department of Transportation, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States is responsible for setting safety standards for autonomous vehicles.
However, the distribution of regulatory authority between the federal and state states may lead to divergences. For example, the federal government requires that airbags must be opened at a certain speed under certain circumstances, and the bumper must withstand the impact of a certain force. When compensating, it is based on state law, which leads to the complexity of the problem.
Another point, compliance with federal safety standards does not guarantee that you will not be responsible for traffic accidents. Because state-level insurance and liability rules tend to be higher than federal safety standards.
Although the federal government has begun to introduce liability and insurance rules for autonomous vehicles, this is not mandatory. It just provides some basic rules. For example, if you want to know how much premium you need to pay to test self-driving cars in Arizona, this question should be answered by an Arizona lawyer, not a federal lawyer.
4. Security and accountability: Alabama as an example
In the early days of the development of self-driving cars in the United States, many states required cars to have auxiliary parking functions, so L3 and L4 level autonomous driving technology was approved. In most states, fully self-driving cars (or L5 level self-driving cars) are still in the testing phase and are not allowed to drive on public roads.
When these restricted L5 level autonomous vehicles are tested in some places, they need to be equipped with drivers or remotely monitor the autonomous vehicles.
Some states have regulated self-driving cars beyond the simple first-generation stage, and have begun to address more complex issues. For example, some states in the United States are discussing V2V communication technology and how to solve this problem within the legal framework of the state. This is the future development goal of autonomous vehicles and the industry.
The Alabama Senate of the United States has introduced a legislation (Alabama Senate Bill 125), which defines truck platoons, whose purpose is to determine the exemption of the highway traffic safety rules for autonomous vehicles or exception.
Under the guidelines of the federal government and the safety regulations of the state government, the car must keep a safe distance from the car. Therefore, the police will issue a ticket when it is too close to the car. The above-mentioned bill provides an exemption system for truck platoons, and believes that the safety distance can be shorter.
According to the provisions of the Act, if the truck is engaged in electronic brake coordination or meets other requirements stipulated by the Ministry of Transport, it will not be subject to the minimum distance between the truck and the vehicle. This means that when the truck platoon violates the minimum following distance, the police have no right to issue a ticket.
We will see a lot of similar examples, because the traditional driving rules are designed for human drivers. So for autonomous vehicles, there will also be more exemptions or changes to existing rules.
In the early days of technological development, the laws between the US states were very different and varied. For technology developers, the difficulty lies in tracking the laws of each state in a timely manner under the current legal system to make the designed system meet the requirements.
In the above cases, there are two possibilities to comply with the rules. One possibility is to adopt the lowest common denominator strategy.
For example, if the state of Colorado stipulates that the minimum following distance for truck rows is 8 feet, but in Alabama, it is 10 feet, then in accordance with the minimum common standard strategy, the design of an automated driving system can take 10 feet throughout the United States Follow the car safely, although the requirements in other states may be shorter.
Another possible method is to design an automatic driving system that can sense the area and adjust it according to local regulations. To enable trucks to perceive the area where they are located and adjust the following distance when crossing the state border, a very complicated network system is required. This is equivalent to the "localization" of the autonomous driving system.
From the perspective of system design, if you consider testing in the United States, you will have to consider the above issues and incorporate them into the system design. Testers can either choose the lowest common standard strategy, or incorporate an interstate awareness system in the system design to achieve localization.
This is a unique feature of the US regulatory system. With regard to the unevenness of state regulations, the federal government may think that the current rules are too confusing, so rules have been issued to replace state regulations. For example, the minimum safety distance is 8 feet, and this rule applies to all states. This is the principle of federal preemployment (federal preempTIon).
This is another way to deal with the complex regulatory environment in the United States beyond the technical level. Therefore, the traffic safety department may recommend that Congress pass a national-level safety following distance standard, which provides a third policy-level solution. Of course, this is just an example. The US regulatory system will affect the design and development of self-driving cars, and US companies need to deal with this properly.
Of course, at the international level, there is also the issue of international coordination. If China, Germany, and Brazil all have regulations for safe distance to the car, they will face the same problem.
In addition, Alabama's exemption for truck platoons also involves liability issues. If the trucks in a group of trucks are owned by different companies and a failure occurs. Under the responsibility system of most states, if the truck platoon complies with the safe following distance, this will become a factor in reducing liability.
Therefore, the safe following distance will not only affect the vehicle's exemption from fines, but also affect the standard for determining liability in the event of a traffic accident. Therefore, compliance with state highway laws can help reduce the cost of accidents because it shows that you are following best practices.
5. China's regulatory system is more conducive to coordination between departments
China has more centralized and top-down regulatory characteristics. The National Development and Reform Commission of China announced a three-year plan in December 2017 to make autonomous driving technology a national priority.
In January 2018, the National Development and Reform Commission organized a study and drafted the "Smart Car Innovation Development Strategy", pointing out that by 2020, China's standard smart car technology innovation, industrial ecology, road network facilities, regulations and standards, product supervision and information security system The framework is basically formed. Smart cars account for 50% of new cars. Positive progress has been made in the construction of intelligent road traffic systems. The coverage of automotive wireless communication networks (LTE-V2X) in large cities and highways has reached 90%, and Beidou high-precision space-time services have achieved full coverage.
By 2025, the technological innovation, industrial ecology, road network facilities, regulatory standards, product supervision, and information security system of Chinese standard smart cars will be fully formed.
In China, the link between promoting economic development and regulation is closer, and when determining whether to comply with regulatory regulations, you only need to refer to a unified standard. In the United States, the national security department is more concerned about reducing accidents and ensuring the safety of drivers. This function is often separated from the United States Department of Commerce and the Department of Transportation, so there are many separate functional departments in the United States.
The advantage of China's centralized regulatory system is that better coordination can be achieved between different functional departments. In the United States, there is a lack of coordination, such as network facilities and security standards. In the United States, network facilities may follow the development of autonomous vehicles, rather than lead its development. This will mean that some vehicles will have to operate without infrastructure.
When it enters an area where network facilities are enabled, it must be able to sense it. There is a division of responsibilities in the management of American highways. Local highways are usually managed by municipal governments, while state highways and federal highways are managed by state and federal governments, respectively. Therefore, at the government level, it is a bit complicated to implement a network on all highways.
This is why all sensor networks in the United States are built by private companies because they cannot wait for government coordination.
2. The second generation of autonomous driving technology:
Vehicle collaboration, intellectual property layout, system opening and closing issues
The second generation of self-driving cars is more discussed in the United States. The main benefits of automatic driving technology are coordination between vehicles and interaction between vehicles and road systems, and coordinated driving saves a lot of resources. In terms of fuel efficiency, it is estimated that compared with truck drivers, truck platoon may save 25% of fuel costs.
In the hundreds of millions of miles traveled, the fuel cost savings will be considerable. But we also need to promote innovation. At present, the issues of intellectual property rights and the opening and closing of systems in vehicle collaboration have not been sufficiently considered.
1. The coordination of autonomous vehicles involves intellectual property issues and the opening and closing of the system
People don't think much about the relationship between closed systems and open communication systems. The functions of the self-driving car are internal and external.
Internal functions include automobile sensing, processing, and decision-making functions. Internal functions enable autonomous vehicles to make autonomous decisions; external functions refer to the interaction of autonomous vehicles with other vehicles or public infrastructure Function, which can enable autonomous vehicles to coordinate and comply with regulatory rules.
In order to realize external functions, there must be an open component module. A completely open platform means that all the functions of the vehicle are written in publicly available code, which is not conducive to enterprises to maintain a competitive advantage.
Therefore, if a technology plays a decisive role in the functions of self-driving cars, such as functions such as perception path prediction and vehicle autonomous decision-making, companies may be unwilling to disclose them.
Take the Lidar Detection System (LIDAR) as an example, which contains many components, which is also a significant piece of the trade secret pool of Waymo and Uber, and also a key area of ​​corporate research. Enterprises want to maintain their competitive advantage through their leading position in the development of LIDAR systems.
So for this part of the vehicle system, there is no need to disclose it for free. But on the other hand, some modules are needed in the vehicle to communicate with other vehicles or infrastructure. This is also one of the advantages of automatic driving system design. Therefore, the question is how to determine the boundary between the internal and external functions in order to maintain the unique features of the automatic driving system.
When the vehicle is driving, it must adjust its own parameters according to other vehicles or public systems. The public system must be able to issue an interrupt signal when there is an emergency. The car needs to make a decision, and then transmit the decision result to the public system, and the two interact.
How to transmit the decision of perception data and intelligent system to the external system while maintaining the exclusiveness of the system technology is a problem that people do not consider much.
In this regard, the connection between public agreements and internal proprietary features is very important. Some public standards may be required in the design of vehicle-to-vehicle and public facility interaction. With this open standard, vehicles can interact with each other. Therefore, some principles are needed to clarify which parts should be proprietary, which is very important.
2. Internal proprietary system-Take the black box as an example
In terms of accident liability, the black box of the autopilot system will involve the issue of proprietary parts. The black box requires very detailed records of all internal perception data and decisions.
But generally speaking, black boxes are only available when an accident occurs. Therefore, most aviation black boxes are designed to only be disassembled and analyzed in the event of an accident. Black boxes are also needed in autonomous driving systems to record the details of perception and decision-making.
However, access to black boxes should be restricted and generally not available to the public to ensure that proprietary algorithms are not disclosed to the public unless the autonomous driving proprietary algorithm causes an accident. Therefore, the black box data that proves the safety of the vehicle should be recognized as proprietary data by the investigating agency.
3. Open protocols enable companies to interact externally while maintaining proprietary technology
From the perspective of intellectual property rights, the company hopes that its researchers will develop a tool with a competitive advantage, and hope that the cars it sells are safer and more efficient. Enterprises need to maintain a competitive advantage, but vehicles need to communicate with vehicles and public facilities of other competing enterprises.
The open model means that companies will dedicate their technology to the public and give up patent rights. So finding a balance between maintaining a competitive advantage and promoting coordination is an important issue.
There is a better way for companies to maintain some proprietary technology without sharing it, and that is a public agreement. The coordination between public technology and proprietary technology is complex. For example, one of the benefits of coordinated self-driving cars is that in the future, we can use infrastructure to control road congestion and assign highway access based on public interest guidelines.
For example, if we have a period of heavy traffic like Russia, and we have a dedicated self-driving car channel, then we have several ways to adjust the opening of the channel.
One is an auction system similar to the real-time search advertising system. Therefore, in this case, the vehicles will compete with each other to see who is willing to pay a higher fee, or to determine the authorization of the vehicle based on the value of the goods or the importance of the passengers, so that the proprietary aspects of the vehicle may not be so important Too. It is important that the bidding agreement is consistent with the infrastructure. In this way, all vehicles can be bid.
However, there is another way to adjust. For example, the opening of the road can be controlled according to the fuel consumption rate or the number of passengers in the car.
So we have some data that must be communicated from the car to the infrastructure. Similarly, data must be passed from a proprietary component. If your car's fuel consumption rate is very advantageous, in order to transfer these data to the public communication system, you must access the private part of the car.
Therefore, an interactive system is needed so that data can be safely transferred from the internal system to the external system to achieve coordination. So achieving the benefits of vehicle collaboration while maintaining exclusiveness is a key issue.
4. Intellectual property layout of autonomous driving technology
The intellectual property layout of enterprises for self-driving cars is not many at present, but this is very important. Through the intellectual property layout, you can gain a deeper understanding of the patent portfolio owned by competitors. But companies not only need to pay attention to the patent layout of Chinese companies, but also to track the models of countries such as the United States and Europe, because foreign countries are also studying this.
The most important data right now is the published patent application, because this information is available early in the study. Patent authorization takes longer and has a lag. In this regard, China also has an advantage.
In China, utility models do not need to undergo substantive examination by the Patent Office, so authorization is faster and easier, and can help companies strengthen intellectual property rights. Moreover, utility model patents can also be converted into invention patents. Of course, these are just some basic research. The patent pool may be another type worth studying.
In addition, companies can track individual inventors and how they flow through the company's internal R & D team; at the same time, if they see a combination of inventors, it may indicate that two teams with different professional capabilities are assigned to work together.
So if the AI ​​team is working with the positioning team, it means that they are trying to integrate complex geographic locations into the AI ​​system. From the hot map, we can understand the enthusiasm of each inventor. There are many ways to decompose data in the research pattern matrix.
In addition, companies can track the areas where competitors apply for patents. If companies start to apply for a patent in a different country, this may mean that they find the study more valuable.
The above is what the patent analysis team needs to do.
When an enterprise carries out patent layout in a complicated way, it can build a patent blueprint. Companies can create a large database to display all patents in the autonomous driving category. This allows companies to clearly see the focus of their research, as well as the advantages and vulnerabilities of their patent layout compared to other companies.
At the current stage of development, these loopholes have little effect. But when the commercialization of self-driving cars becomes a reality, it may trigger litigation. Therefore, the patent blueprint allows companies to understand where they may be attacked and develops a patent strategy to solve this problem.
A common strategy is that if you find a gap in the patent blueprint, you can track the startup companies that have failed in the general economy. They have a large number of patents in the business process. At this time, companies can develop an acquisition strategy to acquire the patents of those failed companies Combination to fill in the blanks of your company's patent blueprint.
This will be very helpful in the future, and the sales value of patents at this time may be much cheaper than their R & D value. Sometimes a valuable team is found, instead of just discovering patents, companies can buy this team and add them to the company's R & D team.
3. Three generations of autonomous driving technology:
Impact of technological development on employment
1. Technology development will produce substitution effect in the short term, but in the long run it will still promote employment
China's economic growth and job creation have been very strong in the past two or three decades. However, in Western countries, economic growth and employment growth are relatively slow, and the impact of autonomous driving technology on labor and employment will be a very important issue.
So now there are some studies trying to assess the overall effect of artificial intelligence and the impact of robots and self-driving cars on employment in more mature Western countries.
When self-driving cars are commercialized, they may encounter some resistance or receive public policy attention in the field of labor and employment. Traditionally, in a medium-growth economy, new technologies always produce substitution effects, causing a large number of people to lose their jobs.
Therefore, in the short term, the substitution of artificial intelligence for humans will cause some public policy resistance. But in the long run, because economic growth always promotes employment, people will always find a job.
In a study of factory robots that began in 2005, it can be seen that economic growth always creates jobs. However, in the short term, there will be a substitution effect and the level of work skills will be reduced. Simply put, autonomous driving systems replace truck drivers, so they may end up working in gas stations, auto parts sales shops or coffee shops.
However, this does not mean that companies cannot launch new technologies, but from the perspective of social impact, companies need to understand that such reactions will occur. The enterprise does not need to change what it is doing, it just needs to make more preparations for it.
2. Need to explain to people the positive impact of technological development
For enterprises, autonomous driving technology must face the third-generation social impact. The typical way to solve this problem is that companies can sponsor some research on employment substitution and try to find a balance between costs and benefits.
People need to understand the positive aspects of technological development. For example, autonomous driving technology will bring bus drivers unemployed, and it will also make many middle-income employees live closer to Silicon Valley, Google, etc., because the commuting range will increase. People can go to work farther away or work on the way to and from work, but they can buy a house farther away from the work place.
People tend to feel the losses caused by technological development more easily, but the benefits brought by it are less conceivable, which is the same as the accident problem. Therefore, it needs to be explained. A good example of this is the commercial aviation industry.
Commercial aviation is now much safer than driving, but if you look back forty or fifty years, many people will worry about the plane crash. In this regard, the industry has done a good job. First, they have improved safety; second, they have explained to people well. So now it seems that aviation is a new technology and it will make people afraid seems to be a long time ago.
In the future, people's views on white driving technology will also change, but it is still in the early stage of development, so companies need to be sensitive to people's psychological changes.
4. The ethical issues faced by autonomous driving technology: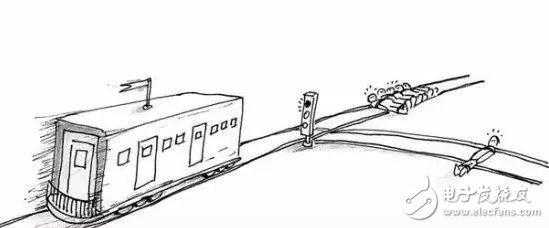
Is the "tram problem" solvable?
There are many versions of the tram problem, but the most basic assumption is that there is a tram running on the track, the front track has a fork, and there are people on both sides of the track. You control the tram switch, at this time you need to choose which track the tram should go to.
There have been many works on the tram problem, but there is no consensus on its solution. Utilitarians may think that people with high income should be preserved and kill others, while Kantists may think that as long as you pull the switch, it is already wrong. The correct way is not to touch the switch , That is, human intervention is wrong.
Judging from some survey data, an interesting phenomenon is that there are some cultural differences in the findings of the tram problem. So one choice may be made based on some cultural values, and another choice may be made based on other cultural values.
For example, some cultures are more utilitarian, while others are more inclined to Kantianism. So there is no universally accepted answer to this question. The consensus reached on the tram problem will vary from culture to culture, and sometimes even between groups of different ages and educational levels.
In addition, there is a solution, which is to set up a rotating directory in the self-driving car. When the car comes, it will randomly choose a program, but this program will also cause controversy.
Therefore, for self-driving cars, the tram problem will always be controversial, because a clear choice must be made and coded. So on this issue, autonomous driving technology will always be criticized, because engineers are writing ethical codes into the code.
There are many studies on the trade-offs of safety design. For example, for the purpose of insurance actuarial, how is human life measured? These data can provide reference.
In system design, there is some consensus on this cost-benefit analysis. But even so, there are still some philosophers who think that the valuation of life is wrong. So as long as you make a choice, you will always be criticized.
So designers of autonomous driving systems cannot win this issue. Therefore, we can solve this problem from another angle. If you design a system, do n’t say that you inevitably choose to hit one of the two people, but describe it as designing a system that can calculate the probability of not killing anyone.
So even if you know that in some cases it will cause death, do not describe the algorithm as choosing to kill one of the two people, but describing it as choosing a best practice that will not cause any death. This approach may not be so controversial. However, if this question is left to a philosopher for discussion, it may never be answered.
Flat Twin Cables
they are suitable for power & lighting circuits and building wiring. Also suitable for use as an earth wire the internal wiring of appliances and apparatus.
- Standard applied: BS 6004
- U0/U: 300/500V
- Certification: Third party test reports available
- Flame retardant or fire resistance or Low smoking and Halogen free or other property can be available
Flat Twin Cables,Flat Twin Wires,Outdoor Electrical Cable Types,Twin Flat Flexible Cable
Shenzhen Bendakang Cables Holding Co., Ltd , https://www.bdkcables.com