The proximity sensor is a general term for a sensor that does not require contact with a detection object for detection, instead of a contact detection method such as a limit switch. It can convert the movement information and presence information of the detection object into electrical signals.
The detection method for conversion to an electric signal includes a method of detecting an eddy current generated in a metal body to be detected by electromagnetic induction, a method of changing a capacity of an electric signal caused by approaching a sample, a method of guiding a rock, and a guide switch. . It consists of an inductive type, an electrostatic capacity type, an ultrasonic type, a photoelectric type, and a magnetic type.

The proximity sensor is an alternating magnetic field generated by the vibrator. When the metal target approaches the magnetic field and reaches the sensing distance, eddy current occurs in the metal target, thus causing the vibration to attenuate, so that the vibrator close to the sensor stops. The vibration of the vibrator of the proximity sensor and the change of the vibration stop are processed by the post-amplifier circuit and converted into a switching signal, which triggers the drive control device, thereby achieving the purpose of non-contact detection of the proximity sensor. This is how the proximity sensor works.
Proximity sensor classificationThe proximity sensor is divided according to the working principle:
High-frequency oscillation type, capacitance type, induction bridge type, permanent magnet type and Hall effect type.
According to the principle of operation, it can be divided into three categories:
The high-frequency oscillation type using electromagnetic induction uses a magnetic type of a magnet and a capacitance type using a capacitance change.
According to the detection method:
General purpose: mainly detecting ferrous metal (iron)
All metal types: detect any metal within the same detection distance.
Non-ferrous metal type: mainly for the detection of non-ferrous metals such as aluminum
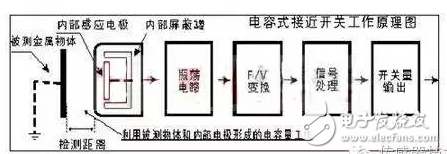
How different types of proximity sensors workCapacitive proximity sensor works: Capacitive proximity sensor consists of a high-frequency oscillator and an amplifier. A capacitor is formed between the detection surface of the sensor and the ground. It participates in the oscillation circuit and starts to oscillate. When the object approaches the sensor detection surface, the capacitance of the loop changes, causing the high frequency oscillator to oscillate. The two states of oscillation and stoppage are converted into electrical signals that are converted into binary switching signals by an amplifier.
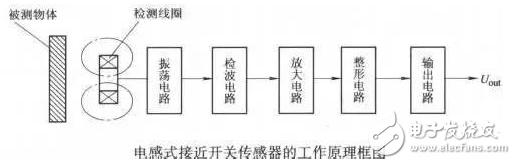
The working principle of inductive proximity sensor: Inductive proximity sensor consists of high frequency oscillation, detection, amplification, trigger and output circuit. The oscillator generates an alternating electromagnetic field on the sensor detection surface. When the metal object approaches the sensor detection surface, the eddy current generated in the metal absorbs the energy of the oscillator, so that the oscillation is weakened and the vibration is stopped. The oscillation and oscillation of the oscillator are converted into electrical signals and converted into binary switching signals by shaping amplification, which are output after power amplification.
The working principle of the high-frequency oscillating proximity sensor: consists of an LC high-frequency oscillator and an amplifier processor circuit. When a metal object approaches the oscillating sensor head, eddy current is generated, so that the oscillation capability of the proximity sensor is attenuated, and the parameters of the internal circuit are changed. This identifies the presence or absence of a metal object, which in turn controls the on or off of the switch.
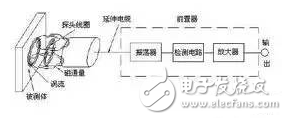
The working principle of all metal sensors: All metal sensors are basically high frequency oscillation type. Like the normal type, it also has an oscillating circuit in which the energy loss caused by the induced current flowing in the target affects the oscillation frequency. When the target approaches the sensor, the oscillation frequency increases regardless of the metal type of the target. The sensor detects this change and outputs a detection signal.
The working principle of the non-ferrous metal sensor: the non-ferrous metal sensor is basically a high-frequency oscillation type. It has an oscillating circuit in which the energy loss caused by the induced current flowing in the target affects the change of the oscillation frequency. When a non-ferrous metal object such as aluminum or copper approaches the sensor, the oscillation frequency increases; when a ferrous metal object such as iron approaches the sensor, the oscillation frequency decreases. If the oscillation frequency is higher than the reference frequency, the sensor outputs a signal.
The working principle of the universal proximity sensor: the coil L in the oscillating circuit generates a high frequency magnetic field. When the target is close to the magnetic field, an induced current (eddy current) is generated in the target due to electromagnetic induction. As the target approaches the sensor, the induced current increases, causing the load in the oscillating circuit to increase. Then, the oscillation is weakened until it stops. The sensor detects the change in the oscillation state by the amplitude detecting circuit and outputs a detection signal.
PET Sheet Roll Material,PET Screen Protector Raw Material,PET Raw Material
Guangdong Magic Electronic Limited , https://www.magicmax.cc